Company Profile
Contact Information:
Location:
Anritsu Introduces the IQ Fiber Master™ MT2780A
Anritsu Introduces Industry’s First 43.5 GHz 1-Port VNA Family
Anritsu Intros 5G Protocol Test Functionality
Anritsu Intros ONA for High Speed Device Testing
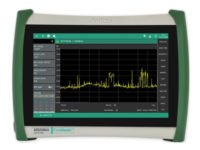
Anritsu Adds RTSA to Field Master Pro
Anritsu to Showcase VNA-Based Test Solutions at EuMW 2019
Anritsu Announces BLE 5.1 AoA/AoD Support
Anritsu Strengthens 5G NR PCT Leadership
Anritsu, ETS-Lindgren Launch 5G NR OTA Solution
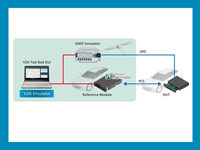
Anritsu Adds IMS Evaluation Functions to MD8475B
Anritsu's Advanced VNA Solutions on Display at IMS2019
Qualcomm Using Anritsu Solution for 5G Testing
Mulder Appointed President and CFO of Anritsu Co.
LG U+ Adopts Anritsu MT1000A for 5G Rollout
Anritsu Earns First 5G NR PCT Validation from GCF
Anritsu, Qualcomm Complete 5G Standalone Connection Test
Anritsu Introduces W1 Components with Coverage from DC to 110 GHz
Anritsu MT8000A Supports MediaTek 5G Chipsets
Anritsu Adds eCPRI, RoE Support to Field Testers
Anritsu Rolls Out 6CA Multi-Gigabit LTE Test Solution
Anritsu Partners with Trescal in The Netherlands
Anritsu Appoints Comtec for UK Distribution
Anritsu and Autotalks Collaborate on V2X DSRC Test Solution
Anritsu and ETS-Lindgren Announce 802.11 Support
Anritsu to demonstrate range of VNAs at EuMW 2014
Downloads

Modern Architecture Advances Vector Network Analyzer Performance
Modern Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) architectures such as those based on Nonlinear Transmission Line (NLTL) samplers and distributed harmonic generators now offer a beneficial alternative to traditional sampling VNAs. They allow for a simplified architecture and also enable VNAs that are much more cost effective. It is shown that NLTL technology results in miniature VNA reflectometers that provide enhanced performance over broad frequency ranges, and reduced measurement complexity, providing VNA users a unique and compelling solution for their high-frequency measurement needs.
Download
Eliminating the Tradeoffs and Limitations of Your Pulse Measurement Test Solution
Next generation radar systems face multiple difficult demands. The pace and variety of new requirements need multi-use/function/mode adaptive radars, to be used for different applications. This whitepaper reviews existing pulse measurement test methods; discusses advantages/limitations; and introduces new test method that takes advantage of high-speed digitizing architecture, offering the industryâ??s highest resolution/timing accuracy level.
Download
Calculating VNA Measurement Accuracy
Vector Network Analyzers (VNA) are your primary resource when analyzing and characterizing systems and components for RF and Microwave measurements. They are regarded as accurate measuring instruments, however, quantifying the accuracy performance of a VNA in a specific application can be challenging. VNA specifications are a starting point; but, they are based upon very specific calibration and measurement conditions, which are not applicable for many applications.
Download
Understanding VNA Calibration
In this guide, the concept of calibration is presented and discussed in detail. Specific topics to be covered include how to configure the VNA for calibration, types of calibration and calibration kits. A minimal amount of calibration mathematics and theory will also be covered.
Download
Advanced VNA Cable Measurements
This field brief will discuss phase-matching cables, S-parameter definitions as they apply to cable characterization and other cable parameters such as Phase Shift and Group Delay. Advanced Time-Domain measurements will also be presented as enhancements to the well-known Distance-to-Fault (DTF) techniques. In addition, diagnostic tools like the Smith Chart will be briefly described.
Download
Modern VNA Solutions Improve On-wafer Measurement Efficiency
In this white paper we look at the impact of calibration downtime during on-wafer testing and discuss how recent advances enable longer time periods between calibrations.
Download
Optimizing Your Millimeter-Wave Test Capability
Testing at millimeter-wave frequencies brings new and different measurement challenges, so minimizing measurement uncertainty is critical in the development of these new technologies. This white paper discusses the challenges associated with millimeter-wave testing and how to optimize your Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) measurement capability to provide the confidence required to make performance/cost tradeoffs.
Download
Superposition vs. True Balanced: What's Required for Your Signal Integrity Application
The True Balanced/Differential technique uses two sources to create actual differential and common-mode stimuli, hence the shortened name true-balanceÂ. This white paper offers guidance to signal integrity designers on the differences between these approaches and which one may best fit their need.
Download
Making successful, confident NF measurements on Amplifiers
The Anritsu VectorStars Noise Figure Option 041 enables the capability to measure noise figure (NF), which is the degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio caused by components in a signal chain. The NF measurement is based on a cold source technique for improved accuracy. Various levels of match and fixture correction are available for additional enhancement. VectorStar is the only VNA platform offering a Noise Figure option enabling NF measurements from 70 kHz to 125 GHz. It is also the only VNA platform available with an optimized noise receiver for measurements from 30 to 125 GHz.
DownloadNoise Figure Measurements
The Anritsu VectorStar’s Noise Figure – Option 041 enables the capability to measure noise figure (NF), which is the degradation of the signal-to-noise ratio caused by components in a signal chain. The NF measurement is based on a cold source technique for improved accuracy.
DownloadHigher Data Rates Require New De-embedding Techniques
Higher data rates can create challenges for traditional de-embedding techniques. As frequencies approach 70 GHz or even 110 GHz, errors related to fixturing can be greater than those of the “device under test” or DUT.
DownloadLow Noise Amplifier Testing Challenges
Designers, modelers, and manufacturers of RF and microwave frequency amplifiers used in applications such as radar, wireless communication, or high-speed digital communication systems at either the wafer-level or as a packaged part face many test challenges.
DownloadSignal Integrity- Frequency Range Matters!
Accurate measurements are needed to better understand higher order harmonics, as will new challenges related to conductor skin effects and dielectric losses on PC boards, along with the design trade-offs related to choices of vias, stackups, and connector pins.
DownloadSuperposition vs. True Balanced: What's Required for Your Signal Integrity Application
Signal Integrity applications commonly utilize balanced/differential transmission lines which are typically characterized using vector network analyzers (VNA). There are two approaches to performing these measurements and the selection of the best method depends on what you need to measure.
DownloadIntroducing the Anritsu Tracking Generator and CW Generator
The Anritsu Option 20 tracking generator provides state of the art features not seen with other competitive hand-held analyzers. This includes capabilities such as 0.1 dB power step size, a wide dynamic range and a power output flatness of ±1 dB.
DownloadSignal Integrity Measurement Challenges
The instantaneous traffic rates at internet data centers have reached 1 Tbit/s and device interconnects are becoming transmission bottlenecks. Assuring signal integrity at high data rates while minimizing cost requires closing the loop of simulation and measurement during the design stage.
DownloadOvercoming High Speed Interconnect Challenges
Cloud computing, smart phones, and LTE services are causing a large increase in network traffic. The instantaneous traffic rates at internet data centers have reached 1 Tbit/s. To support this increased traffic, speed of IT equipment – such as those used in high-end services in data centers – must be increased.
Download




































 Anritsu revolutionizes the test market with the introduction of the Spectrum Master™ MS2760A family, the world’s first ultraportable, mmWave spectrum analyzers that verify high-frequency designs, including those used in 5G and E-Band applications.
Anritsu revolutionizes the test market with the introduction of the Spectrum Master™ MS2760A family, the world’s first ultraportable, mmWave spectrum analyzers that verify high-frequency designs, including those used in 5G and E-Band applications.  Anritsu Co. released a new version of its award-winning SkyBridge Tools™ Test Manager that supports OTDR measurements to establish the industry’s first comprehensive field test automation tool that supports both RF and optical testing. By reducing test time by as much as 90% and increasing accuracy more than 10 times, SkyBridge Tools dramatically simplifies network installation verification, allowing contractors to close out projects more efficiently, receive prompt payment, and start new projects faster.
Anritsu Co. released a new version of its award-winning SkyBridge Tools™ Test Manager that supports OTDR measurements to establish the industry’s first comprehensive field test automation tool that supports both RF and optical testing. By reducing test time by as much as 90% and increasing accuracy more than 10 times, SkyBridge Tools dramatically simplifies network installation verification, allowing contractors to close out projects more efficiently, receive prompt payment, and start new projects faster. Anritsu Co. expands its field test portfolio with the introduction of PIM Hunter,™ a passive intermodulation test probe that helps field technicians more quickly discover the precise location of external PIM sources at cell sites. Designed for use with Anritsu’s PIM Master,™ Spectrum Master™ and BTS Master™ handheld analyzers, the PIM Hunter test probe enables field professionals to use traditional interference hunting techniques to accurately locate external PIM sources for optimum wireless network performance.
Anritsu Co. expands its field test portfolio with the introduction of PIM Hunter,™ a passive intermodulation test probe that helps field technicians more quickly discover the precise location of external PIM sources at cell sites. Designed for use with Anritsu’s PIM Master,™ Spectrum Master™ and BTS Master™ handheld analyzers, the PIM Hunter test probe enables field professionals to use traditional interference hunting techniques to accurately locate external PIM sources for optimum wireless network performance. Anritsu Co. introduced new software for its
Anritsu Co. introduced new software for its  Anritsu Co. announces that is has earned the 2016 Global Product Line Strategy Award—Manufacturing Test Software for IoT from Frost & Sullivan. In making the announcement, Frost & Sullivan stated that newly released software packages from Anritsu uniquely position the company’s
Anritsu Co. announces that is has earned the 2016 Global Product Line Strategy Award—Manufacturing Test Software for IoT from Frost & Sullivan. In making the announcement, Frost & Sullivan stated that newly released software packages from Anritsu uniquely position the company’s  Anritsu Co. expands its industry leading CPRI test portfolio with the introduction of a BBU Emulation capability for its
Anritsu Co. expands its industry leading CPRI test portfolio with the introduction of a BBU Emulation capability for its  Anritsu Co. introduces the ultraportable Site Master™ S331P, the lightest, smallest, fastest and most cost-efficient Site Master field cable and antenna analyzer ever developed. The S331P provides wireless operators and contractors, DAS installers,and public safety network installers and maintenance professionals with the first pocket-sized headless cable and antenna analyzer that can measure the new LTE-U frequencies.
Anritsu Co. introduces the ultraportable Site Master™ S331P, the lightest, smallest, fastest and most cost-efficient Site Master field cable and antenna analyzer ever developed. The S331P provides wireless operators and contractors, DAS installers,and public safety network installers and maintenance professionals with the first pocket-sized headless cable and antenna analyzer that can measure the new LTE-U frequencies. Anritsu Co. introduces Cellular Module Test Application (CMTA) software for its Signaling Testers MD8475A/B which provides test cases to dramatically simplify testing chipsets and automotive-related telematics modules used in connected car designs and implementation.
Anritsu Co. introduces Cellular Module Test Application (CMTA) software for its Signaling Testers MD8475A/B which provides test cases to dramatically simplify testing chipsets and automotive-related telematics modules used in connected car designs and implementation.  Anritsu Co. introduces CPRI RF measurement capability in its market-leading E series of Site Master™, Spectrum Master™ and Cell Master™ handheld field analyzers that dramatically simplifies and lowers the cost of testing Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) installed atop 4G towers.
Anritsu Co. introduces CPRI RF measurement capability in its market-leading E series of Site Master™, Spectrum Master™ and Cell Master™ handheld field analyzers that dramatically simplifies and lowers the cost of testing Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) installed atop 4G towers. Anritsu Co. introduces the Signaling Tester MD8475B, the world’s first all-in-one test solution supporting up to four component carrier aggregation (4CC CA) and 2x2 MIMO in a single test box. Integrated with the SmartStudio GUI, the MD8475B lowers cost-of-test and reduces space requirements compared to conventional solutions that require several test instruments, providing engineers with a highly efficient tool to conduct tests on chipsets, modules, and mobile platforms integrating the most recent LTE-Advanced specifications.
Anritsu Co. introduces the Signaling Tester MD8475B, the world’s first all-in-one test solution supporting up to four component carrier aggregation (4CC CA) and 2x2 MIMO in a single test box. Integrated with the SmartStudio GUI, the MD8475B lowers cost-of-test and reduces space requirements compared to conventional solutions that require several test instruments, providing engineers with a highly efficient tool to conduct tests on chipsets, modules, and mobile platforms integrating the most recent LTE-Advanced specifications. Anritsu Co. expands its Signal Analyzer MS2840A family with the introduction of three models that support the 9 kHz to 3.6 GHz, 6 GHz, and 26.5 GHz frequencies. With the new instruments, Anritsu fills a market void for cost-efficient, high-performance signal analyzers that address the middle frequency ranges, providing an economical solution to accurately measure wireless equipment, oscillators and other components for narrowband applications, land mobile radio, wireless backhaul, radar and automobile electronics.
Anritsu Co. expands its Signal Analyzer MS2840A family with the introduction of three models that support the 9 kHz to 3.6 GHz, 6 GHz, and 26.5 GHz frequencies. With the new instruments, Anritsu fills a market void for cost-efficient, high-performance signal analyzers that address the middle frequency ranges, providing an economical solution to accurately measure wireless equipment, oscillators and other components for narrowband applications, land mobile radio, wireless backhaul, radar and automobile electronics.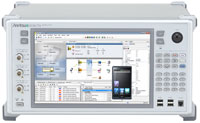 Anritsu Co. announces its Signaling Tester MD8475A now supports 98 percent of conformance test cases (defined as EN16454) for emergency call (eCall) communications modules, expanding the company’s test solution portfolio for connected car designs.
Anritsu Co. announces its Signaling Tester MD8475A now supports 98 percent of conformance test cases (defined as EN16454) for emergency call (eCall) communications modules, expanding the company’s test solution portfolio for connected car designs. Anritsu Co. continues to address the test needs of signal integrity (SI) engineers with the introduction of options for its VectorStar® and ShockLine™ vector network analyzers (VNAs). The VectorStar Eye Diagram and ShockLine Advanced Time Domain (ATD) options are part of the expanding SI capabilities offered by Anritsu and provide SI engineers with improved tools to conduct channel diagnostics and model validation of high-speed digital circuit designs.
Anritsu Co. continues to address the test needs of signal integrity (SI) engineers with the introduction of options for its VectorStar® and ShockLine™ vector network analyzers (VNAs). The VectorStar Eye Diagram and ShockLine Advanced Time Domain (ATD) options are part of the expanding SI capabilities offered by Anritsu and provide SI engineers with improved tools to conduct channel diagnostics and model validation of high-speed digital circuit designs. Anritsu Co. and TRX Systems announce they have entered into a partnership whereby Anritsu’s industry leading handheld analyzers are integrated with a 3D Indoor Location and Mapping solution from TRX Systems to create the industry’s first automatically geo-referenced RF signal mapping solutions.
Anritsu Co. and TRX Systems announce they have entered into a partnership whereby Anritsu’s industry leading handheld analyzers are integrated with a 3D Indoor Location and Mapping solution from TRX Systems to create the industry’s first automatically geo-referenced RF signal mapping solutions. Anritsu Co. introduces software packages for its all-in-one Radio Communication Analyzer MT8821C that support LTE-Advanced UE Downlink (DL) 4x4 MIMO and Downlink Carrier Aggregation (DL CA) 5CCs. The new software packages further strengthen the test functionality of the MT8821C and help create a single-instrument solution that can speed time to market and lower test costs of LTE-Advanced chipsets, smartphones, tablets and M2M modules used in IoT applications.
Anritsu Co. introduces software packages for its all-in-one Radio Communication Analyzer MT8821C that support LTE-Advanced UE Downlink (DL) 4x4 MIMO and Downlink Carrier Aggregation (DL CA) 5CCs. The new software packages further strengthen the test functionality of the MT8821C and help create a single-instrument solution that can speed time to market and lower test costs of LTE-Advanced chipsets, smartphones, tablets and M2M modules used in IoT applications. Anritsu Co. introduces the MA2806A high performance waveguide mixer that can be integrated with its MS2830A Spectrum/Signal Analyzer to create a millimeter-wave (mmWave) measurement solution that eliminates the complexity and uncertainty associated with conventional mmWave signal analysis tools.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MA2806A high performance waveguide mixer that can be integrated with its MS2830A Spectrum/Signal Analyzer to create a millimeter-wave (mmWave) measurement solution that eliminates the complexity and uncertainty associated with conventional mmWave signal analysis tools.  Anritsu Corp. has announced the availability of three new measurement software packages expanding the functions of the MT8870A Universal Wireless Test Set to support manufacturing tests of IoT/M2M applications.
Anritsu Corp. has announced the availability of three new measurement software packages expanding the functions of the MT8870A Universal Wireless Test Set to support manufacturing tests of IoT/M2M applications. Anritsu Corp. released its new high performance waveguide mixer MA2806A to expand millimeter wave measurement solutions. Connecting the new MA2806A to Anritsu’s signal analyzer MS2830A supports spectrum measurements in the 50 to 75 GHz Band (V-Band) currently used by various millimeter wave sensors, WiGig Gigabit Wireless LAN (802.11ad), and broadcast video camera streaming equipment.
Anritsu Corp. released its new high performance waveguide mixer MA2806A to expand millimeter wave measurement solutions. Connecting the new MA2806A to Anritsu’s signal analyzer MS2830A supports spectrum measurements in the 50 to 75 GHz Band (V-Band) currently used by various millimeter wave sensors, WiGig Gigabit Wireless LAN (802.11ad), and broadcast video camera streaming equipment. Anritsu Co. continues to provide the most comprehensive test solutions for the installation and maintenance of legacy and emerging wireless networks with the introduction of a Video Inspection Probe (VIP) measurement mode for its Microwave Site Master™ S820E and Site Master™ S331L cable and antenna analyzers.
Anritsu Co. continues to provide the most comprehensive test solutions for the installation and maintenance of legacy and emerging wireless networks with the introduction of a Video Inspection Probe (VIP) measurement mode for its Microwave Site Master™ S820E and Site Master™ S331L cable and antenna analyzers.  Anritsu Co. introduces an E-band option for its ShockLine™ MS46500B series of 2- and 4-port performance Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) that addresses the market need to lower cost-of-test for E-band components. With the option installed, the MS46500B series can reduce production costs and more efficiently verify the performance of high-frequency passive components, such as antennas, filters, and duplexers during manufacturing.
Anritsu Co. introduces an E-band option for its ShockLine™ MS46500B series of 2- and 4-port performance Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) that addresses the market need to lower cost-of-test for E-band components. With the option installed, the MS46500B series can reduce production costs and more efficiently verify the performance of high-frequency passive components, such as antennas, filters, and duplexers during manufacturing. Anritsu Co. introduces two options for its MN4765B series of O/E calibration modules that help to create a highly accurate, flexible and cost-effective solution for the characterization of optoelectronic devices such as modulators, photoreceivers and integrated optical transceiver modules. With these new options, the MN4765B can be used with the MS4640B VectorStar® Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) family to perform optoelectronic measurements up to 70 GHz at both 1310 nm and 1550 nm wavelengths.
Anritsu Co. introduces two options for its MN4765B series of O/E calibration modules that help to create a highly accurate, flexible and cost-effective solution for the characterization of optoelectronic devices such as modulators, photoreceivers and integrated optical transceiver modules. With these new options, the MN4765B can be used with the MS4640B VectorStar® Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) family to perform optoelectronic measurements up to 70 GHz at both 1310 nm and 1550 nm wavelengths. Anritsu Co. announces support for LTE-A 3 Carrier Aggregation (3CA) Carrier Acceptance Test (CAT) requirements at two additional major North American carriers, building on the first announcement of 3CA support for a third carrier in September.
Anritsu Co. announces support for LTE-A 3 Carrier Aggregation (3CA) Carrier Acceptance Test (CAT) requirements at two additional major North American carriers, building on the first announcement of 3CA support for a third carrier in September.  Anritsu Co. expands its Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Measurement System with the introduction of isotropic antennas that provide frequency coverage from 9 kHz to 6 GHz. Compatible with certain LMR Master™, Spectrum Master™, and Cell Master™ handheld analyzers, the new antennas support measurements of EMF radiation to ensure wireless networks are in compliance with various national standards for personal safety established by government regulatory authorities.
Anritsu Co. expands its Electromagnetic Field (EMF) Measurement System with the introduction of isotropic antennas that provide frequency coverage from 9 kHz to 6 GHz. Compatible with certain LMR Master™, Spectrum Master™, and Cell Master™ handheld analyzers, the new antennas support measurements of EMF radiation to ensure wireless networks are in compliance with various national standards for personal safety established by government regulatory authorities. Anritsu Co. enhances its MN4765B series of O/E modules for the MS4640B VectorStar® Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) family that creates a cost-effective and flexible solution for measuring 56 Gb/s components and transceivers used in telecommunications and data communications applications. The MN4765B module, combined with the MS4640B VNA, provides a simplified approach for optoelectronic measurements and is an economical alternative to conventional total-system approaches currently used in R&D and manufacturing environments.
Anritsu Co. enhances its MN4765B series of O/E modules for the MS4640B VectorStar® Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) family that creates a cost-effective and flexible solution for measuring 56 Gb/s components and transceivers used in telecommunications and data communications applications. The MN4765B module, combined with the MS4640B VNA, provides a simplified approach for optoelectronic measurements and is an economical alternative to conventional total-system approaches currently used in R&D and manufacturing environments. Anritsu Co. announces that it has extended the frequency coverage of its MS46322A Series ShockLine™ Economy Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) and MS46122A Series ShockLine Compact VNAs to 43.5 GHz. By supporting the higher frequency, the low-cost VNAs can efficiently conduct S-parameter and time domain measurements on RF and microwave passive devices up to 43.5 GHzin a variety of cost-sensitive engineering, manufacturing and university testing applications.
Anritsu Co. announces that it has extended the frequency coverage of its MS46322A Series ShockLine™ Economy Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) and MS46122A Series ShockLine Compact VNAs to 43.5 GHz. By supporting the higher frequency, the low-cost VNAs can efficiently conduct S-parameter and time domain measurements on RF and microwave passive devices up to 43.5 GHzin a variety of cost-sensitive engineering, manufacturing and university testing applications. Anritsu Co. introduces a CPRI RF Measurement option for its BTS Master™ handheld base station analyzer family that can significantly reduce the operational expense (OpEx) associated with troubleshooting interference at base stations. Featuring best-in-class sweep speed and unique test capabilities, the BTS Master-based CPRI RF measurement test set allows field engineers and technicians to conduct accurate RF measurements on Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) while remaining at ground level, eliminating the considerable expense and time associated with calling a tower crew to conduct interference measurements.
Anritsu Co. introduces a CPRI RF Measurement option for its BTS Master™ handheld base station analyzer family that can significantly reduce the operational expense (OpEx) associated with troubleshooting interference at base stations. Featuring best-in-class sweep speed and unique test capabilities, the BTS Master-based CPRI RF measurement test set allows field engineers and technicians to conduct accurate RF measurements on Remote Radio Heads (RRHs) while remaining at ground level, eliminating the considerable expense and time associated with calling a tower crew to conduct interference measurements. Anritsu Co. announces that its ME7873LA LTE-Advanced RF Conformance Test System has obtained the world's first LTE 3CA PTCRB certification. By obtaining PTCRB certification for 3CA, the ME7873LA supports deployment of LTE 3CA downlink, expected to be available in North America by the end of the year.
Anritsu Co. announces that its ME7873LA LTE-Advanced RF Conformance Test System has obtained the world's first LTE 3CA PTCRB certification. By obtaining PTCRB certification for 3CA, the ME7873LA supports deployment of LTE 3CA downlink, expected to be available in North America by the end of the year. Anritsu Co., the global leader who introduced the first handheld wireless network analyzer 20 years ago, ushers in a new era of field wireless testing with the introduction of Remote Spectrum Monitor, a platform of modular and scalable products that helps operators generate a greater return on their multi-billion dollar spectrum investments and maximizes network capacity to meet consumer demand.
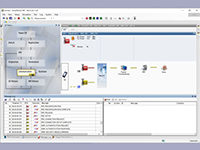
Anritsu Co., the global leader who introduced the first handheld wireless network analyzer 20 years ago, ushers in a new era of field wireless testing with the introduction of Remote Spectrum Monitor, a platform of modular and scalable products that helps operators generate a greater return on their multi-billion dollar spectrum investments and maximizes network capacity to meet consumer demand. Anritsu Co. introduces SkyBridge Tools, a cloud-based trace judgment solution for tower and in-building Distributed Antenna System (DAS) installations that reduces costs and improves ROI. Serving as a data warehouse for contractors who are installing or modifying equipment for network operators, SkyBridge Tools saves time, reduces rework, and makes timely payment more likely by automating the trace judgment process.
Anritsu Co. introduces SkyBridge Tools, a cloud-based trace judgment solution for tower and in-building Distributed Antenna System (DAS) installations that reduces costs and improves ROI. Serving as a data warehouse for contractors who are installing or modifying equipment for network operators, SkyBridge Tools saves time, reduces rework, and makes timely payment more likely by automating the trace judgment process. Anritsu Co. has launched the MT8821C Radio Communication Analyzer for research and development testing of mobile devices.
Anritsu Co. has launched the MT8821C Radio Communication Analyzer for research and development testing of mobile devices. Anritsu Co. introduces a Vector Voltmeter Mode (VVM) for its Microwave Site Master™ S820E – the world’s only handheld cable and antenna analyzer offering coverage up to 40 GHz – that allows the S820E to be used as a drop-in replacement for legacy Vector Voltmeter instruments.
Anritsu Co. introduces a Vector Voltmeter Mode (VVM) for its Microwave Site Master™ S820E – the world’s only handheld cable and antenna analyzer offering coverage up to 40 GHz – that allows the S820E to be used as a drop-in replacement for legacy Vector Voltmeter instruments. Anritsu Co. and EMITE announce that the Anritsu MT8820C radio communication tester has been successfully used in combination with the EMITE E500 reverberation chamber and Anite Propsim FS8 channel emulator to test LTE Carrier Aggregation, using 2x2 MIMO and more realistic isotropic Urban-Macro (UMA) fading profiles.
Anritsu Co. and EMITE announce that the Anritsu MT8820C radio communication tester has been successfully used in combination with the EMITE E500 reverberation chamber and Anite Propsim FS8 channel emulator to test LTE Carrier Aggregation, using 2x2 MIMO and more realistic isotropic Urban-Macro (UMA) fading profiles. Anritsu Co. introduces the MN25208A SmartCal two-port 8.5 GHz auto calibration unit for its ShockLine family of vector network analyzers (VNAs). A plug-and-play calibration unit, SmartCal automatically powers on via a USB connection and loads calibration coefficients from on-board memory, for faster setup and error-free calibrations.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MN25208A SmartCal two-port 8.5 GHz auto calibration unit for its ShockLine family of vector network analyzers (VNAs). A plug-and-play calibration unit, SmartCal automatically powers on via a USB connection and loads calibration coefficients from on-board memory, for faster setup and error-free calibrations. Anritsu Co. introduces the MN4765B O/E Calibration Module for its MS4640B Series VectorStar® vector network analyzers (VNAs) that creates a cost-effective and flexible solution for measuring 40 Gb/s components and transceivers.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MN4765B O/E Calibration Module for its MS4640B Series VectorStar® vector network analyzers (VNAs) that creates a cost-effective and flexible solution for measuring 40 Gb/s components and transceivers. Anritsu Co. introduces the ShockLine™ MS46121A series of 1-port USB Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) that bring the price, performance, and ease-of-use advantages of Anritsu’s patented ShockLine VNA technology to an extremely compact package.
Anritsu Co. introduces the ShockLine™ MS46121A series of 1-port USB Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) that bring the price, performance, and ease-of-use advantages of Anritsu’s patented ShockLine VNA technology to an extremely compact package. Anritsu Co. introduces a unique capture and playback function for its MS2830A and MS269xA Spectrum/Signal Analyzer families that brings the most challenging RF environments from the field into the laboratory or production line.
Anritsu Co. introduces a unique capture and playback function for its MS2830A and MS269xA Spectrum/Signal Analyzer families that brings the most challenging RF environments from the field into the laboratory or production line. Anritsu Co. announces that its MD8475A signaling tester with SmartStudio Manager Windows-based control software now provides multi-operator support for Commercial Mobile Alert System (CMAS) Carrier Acceptance Test (CAT) packages.
Anritsu Co. announces that its MD8475A signaling tester with SmartStudio Manager Windows-based control software now provides multi-operator support for Commercial Mobile Alert System (CMAS) Carrier Acceptance Test (CAT) packages. Anritsu Co. introduces TETRA analyzer and TETRA coverage mapping options to its industry-leading LMR Master™ S412E handheld analyzer. Combining the LMR Master’s best-in-class performance and compact durable design with the new TETRA measuring and analysis tools makes the handheld analyzer the most comprehensive test solution for deploying, installing, and maintaining public safety, transportation, utility and critical communication networks.
Anritsu Co. introduces TETRA analyzer and TETRA coverage mapping options to its industry-leading LMR Master™ S412E handheld analyzer. Combining the LMR Master’s best-in-class performance and compact durable design with the new TETRA measuring and analysis tools makes the handheld analyzer the most comprehensive test solution for deploying, installing, and maintaining public safety, transportation, utility and critical communication networks.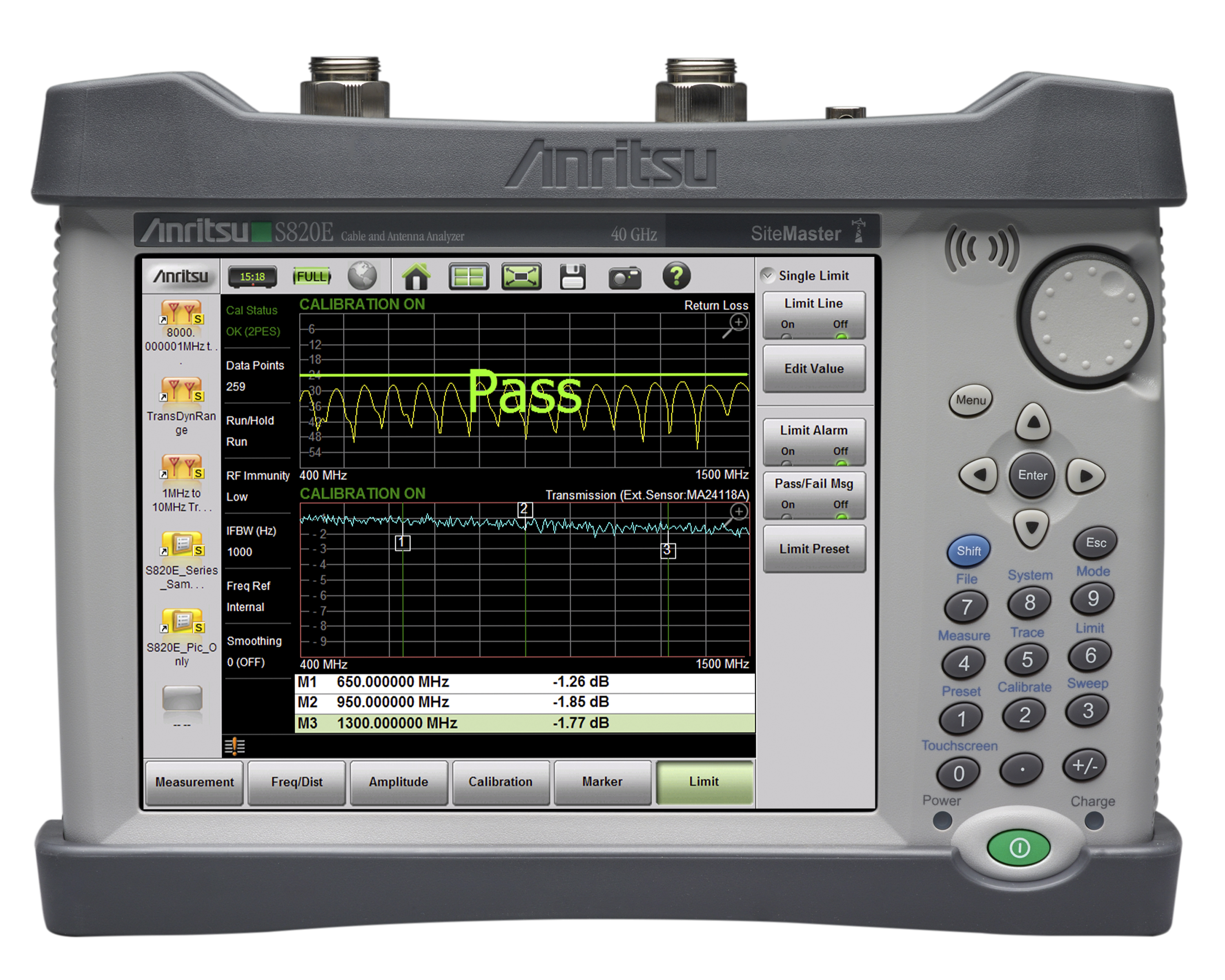 Anritsu Co. introduces the Microwave Site Master S820E, the world’s first handheld cable and antenna analyzer with frequency coverage up to 40 GHz, which continues Anritsu’s leadership position in the handheld analyzer market it established with the first broadband Site Master over 15 years ago.
Anritsu Co. introduces the Microwave Site Master S820E, the world’s first handheld cable and antenna analyzer with frequency coverage up to 40 GHz, which continues Anritsu’s leadership position in the handheld analyzer market it established with the first broadband Site Master over 15 years ago. Anritsu Co. announces a working cooperation with Wild River Technology. The two companies are collaborating to provide test solutions that meet the rigorous test requirements associated with high-speed serial data interconnects, SERDES testing, cables, and backplanes used in NGNs.
Anritsu Co. announces a working cooperation with Wild River Technology. The two companies are collaborating to provide test solutions that meet the rigorous test requirements associated with high-speed serial data interconnects, SERDES testing, cables, and backplanes used in NGNs. Anritsu Co. introduces three frequency options for its industry-leading PIM Master MW82119A Passive Intermodulation (PIM) high-power, battery-operated, portable PIM test analyzer. The new options provide wireless field engineers and technicians with the first battery-operated handheld analyzers that can accurately conduct “top of the tower” PIM measurements in the LTE 800 MHz and UMTS 2100 MHz bands, in addition to the LTE 2600 MHz band.
Anritsu Co. introduces three frequency options for its industry-leading PIM Master MW82119A Passive Intermodulation (PIM) high-power, battery-operated, portable PIM test analyzer. The new options provide wireless field engineers and technicians with the first battery-operated handheld analyzers that can accurately conduct “top of the tower” PIM measurements in the LTE 800 MHz and UMTS 2100 MHz bands, in addition to the LTE 2600 MHz band. Anritsu Co. announces that its PIM Master MW82119A has earned the Frost & Sullivan 2013 Global New Product Innovation Award for PIM Test Equipment. In presenting Anritsu with the award, Frost & Sullivan stated, “the PIM Master MW82119A demonstrates Anritsu’s commitment towards delivering higher value to users of portable PIM test equipment while addressing evolving technological trends in the PIM testing market.”
Anritsu Co. announces that its PIM Master MW82119A has earned the Frost & Sullivan 2013 Global New Product Innovation Award for PIM Test Equipment. In presenting Anritsu with the award, Frost & Sullivan stated, “the PIM Master MW82119A demonstrates Anritsu’s commitment towards delivering higher value to users of portable PIM test equipment while addressing evolving technological trends in the PIM testing market.” Anritsu Co. introduces the MT8220T BTS Master, a multi-function handheld durable tester with all the capabilities network operators, sub-contractors, installers, and regulatory authorities need when measuring base stations. It is the third generation of Anritsu’s field-proven BTS Master family.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MT8220T BTS Master, a multi-function handheld durable tester with all the capabilities network operators, sub-contractors, installers, and regulatory authorities need when measuring base stations. It is the third generation of Anritsu’s field-proven BTS Master family. Anritsu Co. introduces software enhancements to its MD8430A Signaling Tester that make it the first LTE network simulator to support Time Division Duplex LTE (TD-LTE) Carrier Aggregation (CA) test functionality. The MD8430A is the industry’s leading platform for device testing from development to certification and carrier acceptance.
Anritsu Co. introduces software enhancements to its MD8430A Signaling Tester that make it the first LTE network simulator to support Time Division Duplex LTE (TD-LTE) Carrier Aggregation (CA) test functionality. The MD8430A is the industry’s leading platform for device testing from development to certification and carrier acceptance. Anritsu Co. expands its VectorStar family of Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) with the introduction of the MS4640B series.
Anritsu Co. expands its VectorStar family of Vector Network Analyzers (VNAs) with the introduction of the MS4640B series. Anritsu introduces TD-SCDMA signaling test capability for its industry-leading RTD solution. The new software enables chipset and mobile device makers to test their implementation of the 3G mobile communications standard used by China Mobile®.
Anritsu introduces TD-SCDMA signaling test capability for its industry-leading RTD solution. The new software enables chipset and mobile device makers to test their implementation of the 3G mobile communications standard used by China Mobile®. Anritsu Co. announces its MS2720T Spectrum Master™ handheld spectrum analyzer with option 709 has been self-certified to comply with the National Radio Systems Committee requirements for conducting AM and FM measurements.
Anritsu Co. announces its MS2720T Spectrum Master™ handheld spectrum analyzer with option 709 has been self-certified to comply with the National Radio Systems Committee requirements for conducting AM and FM measurements. 
 The MS2720T features a touchscreen, full-band tracking generators to 20 GHz, and best-in-class performance for dynamic range, DANL, phase noise, and sweep speed, providing unprecedented levels of spectrum monitoring, hidden signal detection, RF/microwave measurements, and testing of microwave backhauls and cellular signals.
The MS2720T features a touchscreen, full-band tracking generators to 20 GHz, and best-in-class performance for dynamic range, DANL, phase noise, and sweep speed, providing unprecedented levels of spectrum monitoring, hidden signal detection, RF/microwave measurements, and testing of microwave backhauls and cellular signals. Anritsu Co. introduces the MG3740A analog signal generator that outputs AM/FM/ΦM test signals for evaluation of narrowband analog radio equipment used in public safety networks and private commercial networks.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MG3740A analog signal generator that outputs AM/FM/ΦM test signals for evaluation of narrowband analog radio equipment used in public safety networks and private commercial networks.  Anritsu Co. announces the industry’s first call-based LTE Advanced Carrier Aggregation testing capability that can be integrated into its MD8430A LTE Signaling Tester. The software-only upgrade leverages the four available RFs in the MD8430A, and provides 300 MB/s downlink throughput using two 2x2 MIMO Component Carriers (CCs).
Anritsu Co. announces the industry’s first call-based LTE Advanced Carrier Aggregation testing capability that can be integrated into its MD8430A LTE Signaling Tester. The software-only upgrade leverages the four available RFs in the MD8430A, and provides 300 MB/s downlink throughput using two 2x2 MIMO Component Carriers (CCs).  Anritsu Co. announced it has enhanced its “E” series Site Master and Cell Master handheld analyzers with the introduction of easyTest Tools aimed at helping engineers and field technicians create, deliver, and display cable and antenna analyzer work instructions.
Anritsu Co. announced it has enhanced its “E” series Site Master and Cell Master handheld analyzers with the introduction of easyTest Tools aimed at helping engineers and field technicians create, deliver, and display cable and antenna analyzer work instructions. Anritsu Co. introduced a tracking generator for its Spectrum Master™ MS2711E, MS2712E, and MS2713E models that enhances the overall performance of the handheld analyzers, while making it easier and faster for field technicians to conduct additional measurements.
Anritsu Co. introduced a tracking generator for its Spectrum Master™ MS2711E, MS2712E, and MS2713E models that enhances the overall performance of the handheld analyzers, while making it easier and faster for field technicians to conduct additional measurements.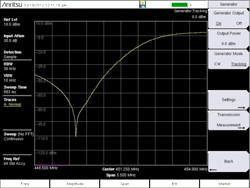 Anritsu Co. introduces a tracking generator for its Spectrum Master™ MS2711E, MS2712E, and MS2713E models that enhances the overall performance of the handheld analyzers.
Anritsu Co. introduces a tracking generator for its Spectrum Master™ MS2711E, MS2712E, and MS2713E models that enhances the overall performance of the handheld analyzers.



















 Anritsu Co. introduces the Signaling Tester MD8475B, the world’s first all-in-one test solution supporting up to four component carrier aggregation (4CC CA) and 2 x 2 MIMO in a single test box. Integrated with the SmartStudio GUI, the MD8475B lowers cost-of-test and reduces space requirements compared to conventional solutions that require several test instruments, providing engineers with a highly efficient tool to conduct tests on chipsets, modules, and mobile platforms.
Anritsu Co. introduces the Signaling Tester MD8475B, the world’s first all-in-one test solution supporting up to four component carrier aggregation (4CC CA) and 2 x 2 MIMO in a single test box. Integrated with the SmartStudio GUI, the MD8475B lowers cost-of-test and reduces space requirements compared to conventional solutions that require several test instruments, providing engineers with a highly efficient tool to conduct tests on chipsets, modules, and mobile platforms. Anritsu Co. released a version of its award-winning SkyBridge Tools™ Test Manager that supports OTDR measurements to establish the industry’s first comprehensive field test automation tool that supports both RF and optical testing. By reducing test time by as much as 90% and increasing accuracy more than 10 times, SkyBridge Tools dramatically simplifies network installation verification.
Anritsu Co. released a version of its award-winning SkyBridge Tools™ Test Manager that supports OTDR measurements to establish the industry’s first comprehensive field test automation tool that supports both RF and optical testing. By reducing test time by as much as 90% and increasing accuracy more than 10 times, SkyBridge Tools dramatically simplifies network installation verification. Anritsu Co. expands its field test portfolio with the introduction of PIM Hunter,™ a passive intermodulation test probe that helps field technicians more quickly discover the precise location of external PIM sources at cell sites. Designed for use with Anritsu’s PIM Master,™ Spectrum Master™ and BTS Master™ handheld analyzers, the PIM Hunter test probe enables field professionals to use traditional interference hunting techniques.
Anritsu Co. expands its field test portfolio with the introduction of PIM Hunter,™ a passive intermodulation test probe that helps field technicians more quickly discover the precise location of external PIM sources at cell sites. Designed for use with Anritsu’s PIM Master,™ Spectrum Master™ and BTS Master™ handheld analyzers, the PIM Hunter test probe enables field professionals to use traditional interference hunting techniques. Anritsu Co. introduced software for its radio communications analyzer MT8821C that creates the industry’s first test solution that supports evaluation of 4 x 4 MIMO 256 QAM RF Rx performance for all DL 3CC CA band combinations with no restrictions on frequency and signal bandwidth combinations. The software provides wireless chipset and UE manufacturers.
Anritsu Co. introduced software for its radio communications analyzer MT8821C that creates the industry’s first test solution that supports evaluation of 4 x 4 MIMO 256 QAM RF Rx performance for all DL 3CC CA band combinations with no restrictions on frequency and signal bandwidth combinations. The software provides wireless chipset and UE manufacturers.
 Anritsu Co. introduces CPRI RF measurement capability in its market-leading E series of Site Master™, Spectrum Master™, and Cell Master™ handheld field analyzers that dramatically simplifies and lowers the cost of testing remote radio heads installed atop 4G towers. The option reduces network OpEx by allowing wireless carrier engineers, technicians and contractors responsible for wireless networks to identify interference sources on the radio uplink at ground level, reducing the use of unnecessary and costly tower climbing crews.
Anritsu Co. introduces CPRI RF measurement capability in its market-leading E series of Site Master™, Spectrum Master™, and Cell Master™ handheld field analyzers that dramatically simplifies and lowers the cost of testing remote radio heads installed atop 4G towers. The option reduces network OpEx by allowing wireless carrier engineers, technicians and contractors responsible for wireless networks to identify interference sources on the radio uplink at ground level, reducing the use of unnecessary and costly tower climbing crews. Anritsu Co. expands its Signal Analyzer MS2840A family with the introduction of three models that support the 9 kHz to 3.6 GHz, 6 GHz, and 26.5 GHz frequencies. With the instruments, Anritsu fills a market void for cost-efficient, high-performance signal analyzers that address the middle frequency ranges, providing an economical solution to accurately measure wireless equipment, oscillators and other components for narrowband applications, and more.
Anritsu Co. expands its Signal Analyzer MS2840A family with the introduction of three models that support the 9 kHz to 3.6 GHz, 6 GHz, and 26.5 GHz frequencies. With the instruments, Anritsu fills a market void for cost-efficient, high-performance signal analyzers that address the middle frequency ranges, providing an economical solution to accurately measure wireless equipment, oscillators and other components for narrowband applications, and more. Anritsu Company continues to address the test needs of signal integrity (SI) engineers with the introduction of options for its VectorStar® and ShockLine™ vector network analyzers (VNAs). The VectorStar Eye Diagram and ShockLine Advanced Time Domain (ATD) options are part of the expanding SI capabilities offered by Anritsu and provide SI engineers with improved tools to conduct channel diagnostics and model validation of high-speed digital circuit designs.
Anritsu Company continues to address the test needs of signal integrity (SI) engineers with the introduction of options for its VectorStar® and ShockLine™ vector network analyzers (VNAs). The VectorStar Eye Diagram and ShockLine Advanced Time Domain (ATD) options are part of the expanding SI capabilities offered by Anritsu and provide SI engineers with improved tools to conduct channel diagnostics and model validation of high-speed digital circuit designs. Anritsu Corp. announced that Amsterdam Internet Exchange (AMS-IX) has selected the MT1100A 100 G/OTU4 Network Master Flex Analyzer. This increases the test and measuring investment that AMS-IX has made with Anritsu following on from the two MD1260A 100G IP/Ethernet analyzers. MT1100A Network Master Flex is designed to meet all of these demands, and to provide all the testing requirements for the second wave of innovation in the 40/100 GbE networks.
Anritsu Corp. announced that Amsterdam Internet Exchange (AMS-IX) has selected the MT1100A 100 G/OTU4 Network Master Flex Analyzer. This increases the test and measuring investment that AMS-IX has made with Anritsu following on from the two MD1260A 100G IP/Ethernet analyzers. MT1100A Network Master Flex is designed to meet all of these demands, and to provide all the testing requirements for the second wave of innovation in the 40/100 GbE networks. Anritsu Company introduces the MS2840A signal analyzer that features broad frequency coverage of 9 kHz to 44.5 GHz and best-in-class close-in SSB phase noise performance. With the high-end performance and frequency coverage that can be extended to the millimeter wave (mmWave) range, the MS2840A is a highly accurate tool to conduct wideband and narrowband measurements on next-generation 4G/5G designs, microwave and mmWave wireless backhaul and more.
Anritsu Company introduces the MS2840A signal analyzer that features broad frequency coverage of 9 kHz to 44.5 GHz and best-in-class close-in SSB phase noise performance. With the high-end performance and frequency coverage that can be extended to the millimeter wave (mmWave) range, the MS2840A is a highly accurate tool to conduct wideband and narrowband measurements on next-generation 4G/5G designs, microwave and mmWave wireless backhaul and more.
 Anritsu Company introduces software packages for its all-in-one radio communication analyzer MT8821C that support LTE-advanced UE downlink (DL) 4 x 4 MIMO and downlink carrier aggregation (DL CA) 5 CCs. The new software packages further strengthen the test functionality of the MT8821C and help create a single-instrument solution that can speed time to market and lower test costs of LTE-advanced chipsets, smartphones, tablets and M2M modules used in IoT applications.
Anritsu Company introduces software packages for its all-in-one radio communication analyzer MT8821C that support LTE-advanced UE downlink (DL) 4 x 4 MIMO and downlink carrier aggregation (DL CA) 5 CCs. The new software packages further strengthen the test functionality of the MT8821C and help create a single-instrument solution that can speed time to market and lower test costs of LTE-advanced chipsets, smartphones, tablets and M2M modules used in IoT applications. Anritsu Corp. is pleased to announce the release of its High Performance Waveguide Mixer MA2806A to expand millimeter-wave measurement solutions. Connecting the new MA2806A to Anritsu’s Signal Analyzer MS2830A supports spectrum measurements in the 50 to 75 GHz band (V-band) currently used by various millimeter-wave sensors, WiGig Gigabit Wireless LAN (802.11ad), and broadcast video camera streaming equipment.
Anritsu Corp. is pleased to announce the release of its High Performance Waveguide Mixer MA2806A to expand millimeter-wave measurement solutions. Connecting the new MA2806A to Anritsu’s Signal Analyzer MS2830A supports spectrum measurements in the 50 to 75 GHz band (V-band) currently used by various millimeter-wave sensors, WiGig Gigabit Wireless LAN (802.11ad), and broadcast video camera streaming equipment. Anritsu Company continues to expand its industry-leading field test portfolio with the introduction of the MS27101A Remote Spectrum Monitor. The most recent edition to Anritsu’s interference detecting tools, the MS27101A can be used with Anritsu’s Vision™ software to create a highly accurate remote solution for government regulators and university lab researchers to identify interference patterns as well as record spectrum history.
Anritsu Company continues to expand its industry-leading field test portfolio with the introduction of the MS27101A Remote Spectrum Monitor. The most recent edition to Anritsu’s interference detecting tools, the MS27101A can be used with Anritsu’s Vision™ software to create a highly accurate remote solution for government regulators and university lab researchers to identify interference patterns as well as record spectrum history. Anritsu is pleased to announce the addition of two frequency solutions to their Shockline MS46500B series of 2 and 4 port vector network analyzers (VNAs). The new models include a unique E-band option for testing and verifying the efficiency of passive components during manufacturing, and a high performing 20 and 40 GHz Microwave option.
Anritsu is pleased to announce the addition of two frequency solutions to their Shockline MS46500B series of 2 and 4 port vector network analyzers (VNAs). The new models include a unique E-band option for testing and verifying the efficiency of passive components during manufacturing, and a high performing 20 and 40 GHz Microwave option. Anritsu Company announces support for LTE-A 3 Carrier Aggregation (3CA) Carrier Acceptance Test (CAT) requirements. The ME7834LA is a scalable GCF, PTCRB, and carrier-validated test system that enables certification of 3G and LTE devices to industry and carrier standards. It provides test coverage for 3GPP 36.523 as well as a wide portfolio of CAT test plans across multiple operators. For existing users of the ME7834L platform, an upgrade path is available with support.
Anritsu Company announces support for LTE-A 3 Carrier Aggregation (3CA) Carrier Acceptance Test (CAT) requirements. The ME7834LA is a scalable GCF, PTCRB, and carrier-validated test system that enables certification of 3G and LTE devices to industry and carrier standards. It provides test coverage for 3GPP 36.523 as well as a wide portfolio of CAT test plans across multiple operators. For existing users of the ME7834L platform, an upgrade path is available with support. Anritsu introduces a CPRI RF measurement option for its BTS Master™ handheld base station analyzer family that can significantly reduce the operational expense associated with troubleshooting interference at base stations. The BTS Master-based CPRI RF measurement test set allows field engineers and technicians to conduct accurate RF measurements on remote radio heads (RRHs) while remaining at ground level.
Anritsu introduces a CPRI RF measurement option for its BTS Master™ handheld base station analyzer family that can significantly reduce the operational expense associated with troubleshooting interference at base stations. The BTS Master-based CPRI RF measurement test set allows field engineers and technicians to conduct accurate RF measurements on remote radio heads (RRHs) while remaining at ground level. Anritsu Co. introduces the MT8821C Radio Communication Analyzer, an all-in-one RF tester with the widest capability for supporting LTE-advanced (LTE-A), as well as all other adopted technologies. The MT8821C supports 2 to 4 G wireless tests, making it a cost-effective single-instrument solution to validate co-existing UEs integrating multiple technologies. Covering 30 MHz to 6 GHz, it can conduct RF TRx tests in compliance with the 3 GPP and 3 GPP2 standards.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MT8821C Radio Communication Analyzer, an all-in-one RF tester with the widest capability for supporting LTE-advanced (LTE-A), as well as all other adopted technologies. The MT8821C supports 2 to 4 G wireless tests, making it a cost-effective single-instrument solution to validate co-existing UEs integrating multiple technologies. Covering 30 MHz to 6 GHz, it can conduct RF TRx tests in compliance with the 3 GPP and 3 GPP2 standards. Anritsu introduces the MA24208A/MA24218A universal USB power sensors that leverage Anritsu’s patented triple path architecture to provide highly accurate, true RMS measurements of CW, multi-tone, and digitally modulated signals up to 18 GHz. Combining a broad measurement range of -60 to +20 dBm with measurement speeds of >1,600 readings/s continuous and >11,000 readings/s buffered, the MA24208A/MA24218A bring a high level of performance to a variety of applications.
Anritsu introduces the MA24208A/MA24218A universal USB power sensors that leverage Anritsu’s patented triple path architecture to provide highly accurate, true RMS measurements of CW, multi-tone, and digitally modulated signals up to 18 GHz. Combining a broad measurement range of -60 to +20 dBm with measurement speeds of >1,600 readings/s continuous and >11,000 readings/s buffered, the MA24208A/MA24218A bring a high level of performance to a variety of applications. Anritsu Company introduces a vector voltmeter mode (VVM) for its Microwave Site Master™ S820E – the world’s only handheld cable and antenna analyzer offering coverage up to 40 GHz – that allows the S820E to be used as a drop-in replacement for legacy Vector Voltmeter instruments. The Site Master S820E combines leading-edge performance, functionality, reporting and durability to meet the most demanding field testing requirements.
Anritsu Company introduces a vector voltmeter mode (VVM) for its Microwave Site Master™ S820E – the world’s only handheld cable and antenna analyzer offering coverage up to 40 GHz – that allows the S820E to be used as a drop-in replacement for legacy Vector Voltmeter instruments. The Site Master S820E combines leading-edge performance, functionality, reporting and durability to meet the most demanding field testing requirements. Anritsu Company introduces Web Remote Tools for its Spectrum Master™ MS2720T handheld spectrum analyzer that allows the instruments to be controlled from any web-enabled device, including laptops, tablets, and smart phones, over an Ethernet link. Web Remote Tools test Remote Radio Heads (RRUs) and other inaccessible radio units at 3G and 4G base stations.
Anritsu Company introduces Web Remote Tools for its Spectrum Master™ MS2720T handheld spectrum analyzer that allows the instruments to be controlled from any web-enabled device, including laptops, tablets, and smart phones, over an Ethernet link. Web Remote Tools test Remote Radio Heads (RRUs) and other inaccessible radio units at 3G and 4G base stations. Anritsu Co. introduced an electromagnetic field (EMF) radiation measurement system for its Spectrum Master™ MS271xE handheld spectrum analyzers and Cell Master™ MT8212E/MT8213E base station analyzers. With the option installed and an Anritsu isotropic antenna attached, the analyzers can be used by field technicians of government regulatory authorities and cellular operators to measure electromagnetic fields, ensuring wireless networks are in compliance with various national standards for personal safety.
Anritsu Co. introduced an electromagnetic field (EMF) radiation measurement system for its Spectrum Master™ MS271xE handheld spectrum analyzers and Cell Master™ MT8212E/MT8213E base station analyzers. With the option installed and an Anritsu isotropic antenna attached, the analyzers can be used by field technicians of government regulatory authorities and cellular operators to measure electromagnetic fields, ensuring wireless networks are in compliance with various national standards for personal safety. Anritsu Co. expands its ShockLine™ family of vector network analyzers (VNAs) with the introduction of the MS46122A series. Incorporating Anritsu’s patented shock line VNA-on-a-chip technology, the MS46122A low-cost full-reversing 2-port VNAs are packaged in a very compact 1U chassis and are optimized for ultra-cost-sensitive test applicatios in manufacturing, engineering, and education environments.
Anritsu Co. expands its ShockLine™ family of vector network analyzers (VNAs) with the introduction of the MS46122A series. Incorporating Anritsu’s patented shock line VNA-on-a-chip technology, the MS46122A low-cost full-reversing 2-port VNAs are packaged in a very compact 1U chassis and are optimized for ultra-cost-sensitive test applicatios in manufacturing, engineering, and education environments. Anritsu Company introduces options for its MD8475A Network Simulator platform that support WLAN Offload smartphone testing, creating an accurate and efficient test solution for verifying mobile devices early in the device integration test process. The MD8475A simulates real-world carrier network implementation of industry-standard WLAN Offload functions.
Anritsu Company introduces options for its MD8475A Network Simulator platform that support WLAN Offload smartphone testing, creating an accurate and efficient test solution for verifying mobile devices early in the device integration test process. The MD8475A simulates real-world carrier network implementation of industry-standard WLAN Offload functions. The MD8430A is a scalable LTE network simulator, with six models ranging from functional test model (FTM) to enhanced test model (ETM), and available software options for both LTE FDD and TDD for any model. The associated rapid test designer (RTD) graphical test software enables quick scripting of tests, with an intuitive user interface as well as available layer 3 and lower-layer libraries.
The MD8430A is a scalable LTE network simulator, with six models ranging from functional test model (FTM) to enhanced test model (ETM), and available software options for both LTE FDD and TDD for any model. The associated rapid test designer (RTD) graphical test software enables quick scripting of tests, with an intuitive user interface as well as available layer 3 and lower-layer libraries. Anritsu Company, as part of its commitment to support global wireless standards, announces that it is the market leader in approved test cases for TD-LTE Carrier Aggregation and is the only test company with Global Certification Forum (GCF)-approved TD-LTE test cases in the IMS Voice over LTE (VoLTE)-related technology of aSRVCC.
Anritsu Company, as part of its commitment to support global wireless standards, announces that it is the market leader in approved test cases for TD-LTE Carrier Aggregation and is the only test company with Global Certification Forum (GCF)-approved TD-LTE test cases in the IMS Voice over LTE (VoLTE)-related technology of aSRVCC. Anritsu Co. introduces a mobile interference hunting system that helps field engineers and technicians locate sources of interference more accurately. Integrating an easy-to-use interface, fast setup times and numerous features to effectively hunt a variety of signal types in multiple RF environments, the comprehensive solution provides wireless carriers, regulatory agencies, and broadcast and satellite operators with a tool that saves time and money.
Anritsu Co. introduces a mobile interference hunting system that helps field engineers and technicians locate sources of interference more accurately. Integrating an easy-to-use interface, fast setup times and numerous features to effectively hunt a variety of signal types in multiple RF environments, the comprehensive solution provides wireless carriers, regulatory agencies, and broadcast and satellite operators with a tool that saves time and money. Anritsu Co. breaks new ground in field wireless test with the introduction of the MW82119B PIM Master™, which combines a 40 W, battery-operated PIM analyzer with a 2 MHz to 3 GHz cable and antenna analyzer, eliminating the need to carry multiple instruments to measure the RF performance of a cell site. It is MIL-STD-810G drop test rated and is designed to withstand transportation shock, vibration and harsh outdoor test conditions.
Anritsu Co. breaks new ground in field wireless test with the introduction of the MW82119B PIM Master™, which combines a 40 W, battery-operated PIM analyzer with a 2 MHz to 3 GHz cable and antenna analyzer, eliminating the need to carry multiple instruments to measure the RF performance of a cell site. It is MIL-STD-810G drop test rated and is designed to withstand transportation shock, vibration and harsh outdoor test conditions. Anritsu Co. addresses the market need for value and performance when testing RF passive devices with the introduction of the ShockLine™ MS46522A 2-port RF VNA family with frequency coverage from 50 kHz to 8.5 GHz. The ShockLine MS46522A VNA is designed for testing passive devices such as cables, connectors, filters, and antennas in a wide variety of engineering, manufacturing and education applications.
Anritsu Co. addresses the market need for value and performance when testing RF passive devices with the introduction of the ShockLine™ MS46522A 2-port RF VNA family with frequency coverage from 50 kHz to 8.5 GHz. The ShockLine MS46522A VNA is designed for testing passive devices such as cables, connectors, filters, and antennas in a wide variety of engineering, manufacturing and education applications. Anritsu Co. establishes a new standard in broadband performance with the introduction of the VectorStar™ ME7838D broadband system that provides industry-best frequency coverage of 70 kHz to 145 GHz in a single sweep using a coaxial test port. The VectorStar ME7838D gives design engineers greater confidence when performing on-wafer device characterization at 70 GHz and beyond.
Anritsu Co. establishes a new standard in broadband performance with the introduction of the VectorStar™ ME7838D broadband system that provides industry-best frequency coverage of 70 kHz to 145 GHz in a single sweep using a coaxial test port. The VectorStar ME7838D gives design engineers greater confidence when performing on-wafer device characterization at 70 GHz and beyond.

 Anritsu Co. announces that its ME7873L RF/RRM Conformance Test System has achieved the world’s first test platform approval criteria (TPAC) for LTE-advanced carrier aggregation (CA). This industry-leading achievement in the Global Certification Forum (GCF) enables wireless device manufacturers to implement certification of devices employing this new technology.
Anritsu Co. announces that its ME7873L RF/RRM Conformance Test System has achieved the world’s first test platform approval criteria (TPAC) for LTE-advanced carrier aggregation (CA). This industry-leading achievement in the Global Certification Forum (GCF) enables wireless device manufacturers to implement certification of devices employing this new technology.  Anritsu Company introduces three frequency options for its industry-leading PIM Master MW82119A Passive Intermodulation (PIM) high-power, battery-operated, portable PIM test analyzer. The new options provide wireless field engineers and technicians with the first battery-operated handheld analyzers that can accurately conduct “top of the tower” PIM measurements in the LTE 800 MHz and UMTS 2100 MHz bands, in addition to the LTE 2600 MHz band.
Anritsu Company introduces three frequency options for its industry-leading PIM Master MW82119A Passive Intermodulation (PIM) high-power, battery-operated, portable PIM test analyzer. The new options provide wireless field engineers and technicians with the first battery-operated handheld analyzers that can accurately conduct “top of the tower” PIM measurements in the LTE 800 MHz and UMTS 2100 MHz bands, in addition to the LTE 2600 MHz band. Anritsu Company introduces the MT8220T BTS Master, a multi-function handheld durable tester with all the capabilities network operators, sub-contractors, installers, and regulatory authorities need when measuring base stations. By providing multiple testing capabilities, including comprehensive Over-the-Air (OTA) measurements to support Remote Radio Heads (RRH) and MIMO, it is well suited for co-siting of new systems with existing networks.
Anritsu Company introduces the MT8220T BTS Master, a multi-function handheld durable tester with all the capabilities network operators, sub-contractors, installers, and regulatory authorities need when measuring base stations. By providing multiple testing capabilities, including comprehensive Over-the-Air (OTA) measurements to support Remote Radio Heads (RRH) and MIMO, it is well suited for co-siting of new systems with existing networks. Anritsu Company announces the availability of LTE Advanced Carrier Aggregation (CA) Measurement Software for its MT8820C RF tester, enabling analysis of leading-edge mobile devices incorporating the new ultra-fast technology evolution. The new option leverages the ParallelPhone Mode (PPMTM) dual-RF capability of the MT8820C to simulate inter-band and intra-band downlink frequency domain duplex (FDD) CA with call processing.
Anritsu Company announces the availability of LTE Advanced Carrier Aggregation (CA) Measurement Software for its MT8820C RF tester, enabling analysis of leading-edge mobile devices incorporating the new ultra-fast technology evolution. The new option leverages the ParallelPhone Mode (PPMTM) dual-RF capability of the MT8820C to simulate inter-band and intra-band downlink frequency domain duplex (FDD) CA with call processing. Anritsu Company introduces the MT8870A universal wireless test set with manufacturing test capability for up to eight user equipment (UE) devices in a single mainframe without the need for external switching. The tester’s basic module includes an integrated vector signal analyzer (VSA), vector signal generator (VSG), and multi-core processor.
Anritsu Company introduces the MT8870A universal wireless test set with manufacturing test capability for up to eight user equipment (UE) devices in a single mainframe without the need for external switching. The tester’s basic module includes an integrated vector signal analyzer (VSA), vector signal generator (VSG), and multi-core processor. Anritsu Company introduces the MG3710A series, a family of innovative vector signal generators that combines high performance and eliminates the need for multiple instruments, thereby reducing operating costs and increasing production yield for designers and manufacturers of multi-system devices and base stations. Its unique design allows the MG3710A to generate test signals based on all leading technologies.
Anritsu Company introduces the MG3710A series, a family of innovative vector signal generators that combines high performance and eliminates the need for multiple instruments, thereby reducing operating costs and increasing production yield for designers and manufacturers of multi-system devices and base stations. Its unique design allows the MG3710A to generate test signals based on all leading technologies. The Anritsu MT8852B Bluetooth Test Set is the market leading RF measuring instrument for design proving and production test of a wide range of products that integrate Bluetooth technology, including; phones, headsets, computers, audio-visual and gaming products as well as modules. In production, a single key press initiates a measurement script that tests a device in less than 10 seconds.
The Anritsu MT8852B Bluetooth Test Set is the market leading RF measuring instrument for design proving and production test of a wide range of products that integrate Bluetooth technology, including; phones, headsets, computers, audio-visual and gaming products as well as modules. In production, a single key press initiates a measurement script that tests a device in less than 10 seconds. Anritsu's family of Spectrum Master handheld spectrum analyzers offers five models to choose from including the industry’s first 32 GHz and 43 GHz models. Models MS2722C, MS2723C, MS2724C, MS2725C, and MS2726C represents the company’s highest performance handheld spectrum analyzers.
Anritsu's family of Spectrum Master handheld spectrum analyzers offers five models to choose from including the industry’s first 32 GHz and 43 GHz models. Models MS2722C, MS2723C, MS2724C, MS2725C, and MS2726C represents the company’s highest performance handheld spectrum analyzers. The BTS Master MT8221B is Anritsu's high performance base station analyzer. From the ground up it has been designed to support 4G standards and installed 2G/3G networks.
The BTS Master MT8221B is Anritsu's high performance base station analyzer. From the ground up it has been designed to support 4G standards and installed 2G/3G networks. The BTS Master MT8221B is Anritsu's high performance base station analyzer. From the ground up it has been designed to support 4G standards and installed 2G/3G networks.
The BTS Master MT8221B is Anritsu's high performance base station analyzer. From the ground up it has been designed to support 4G standards and installed 2G/3G networks. To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field.
To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field. To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field.
To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field. To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field.
To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field. To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field.
To keep up in today's rapidly evolving wireless communications market, you need tools that enable you to efficiently maintain legacy networks in addition to the new 3G and 4G networks now being installed. And with rate of market expansion, you're being required to service more base stations than ever before. This means completing sweeps quickly, performing calibrations instantly, and implementing fast trace naming while in the field. The VNA Master MS202xB/3xB series is a compact handheld multi-function instrument that offers a portable yet powerful vector network analyzer, allowing you to do S-parameter analysis in the field ― anytime, anywhere.
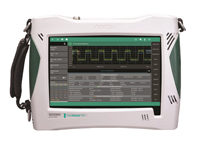
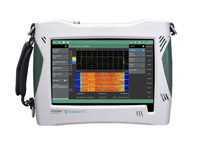
The VNA Master MS202xB/3xB series is a compact handheld multi-function instrument that offers a portable yet powerful vector network analyzer, allowing you to do S-parameter analysis in the field ― anytime, anywhere. The title Grand Master suggests the ultimate level of skill, experience, accomplishment and recognition as best in class. The VNA Master Series is the industry’s highest performance, handheld solution for 2-port, 2-path measurements, anytime, anywhere.
The title Grand Master suggests the ultimate level of skill, experience, accomplishment and recognition as best in class. The VNA Master Series is the industry’s highest performance, handheld solution for 2-port, 2-path measurements, anytime, anywhere. Anritsu’s MS2712E and MS2713E Spectrum Master™ spectrum analyzers are designed to handle the most punishing field conditions and allow you to monitor, locate, identify, and analyze a broad range of cellular, land mobile radio, Wi-Fi, and broadcast signals.
Anritsu’s MS2712E and MS2713E Spectrum Master™ spectrum analyzers are designed to handle the most punishing field conditions and allow you to monitor, locate, identify, and analyze a broad range of cellular, land mobile radio, Wi-Fi, and broadcast signals. The MS2721B handheld spectrum analyzer is designed to conduct highly accurate analysis on the new wave of wireless LAN and cellular signals, including 802.11a, 3G, ultra-wideband, WiMAX, and wireless medical patient monitoring systems.
The MS2721B handheld spectrum analyzer is designed to conduct highly accurate analysis on the new wave of wireless LAN and cellular signals, including 802.11a, 3G, ultra-wideband, WiMAX, and wireless medical patient monitoring systems. Regulatory requirements are growing. You're under increasing pressure to cut costs. And improving system up-time is always a top priority. The MS2711E Spectrum Master helps you do all of this and more.
Regulatory requirements are growing. You're under increasing pressure to cut costs. And improving system up-time is always a top priority. The MS2711E Spectrum Master helps you do all of this and more. The S412E is Anritsu's second generation solution for installing and maintaining public safety systems. Built on Anritsu's ninth generation handheld platform, the S412E combines a high performance receiver / spectrum analyzer with the world's most advanced handheld vector network analyzer plus a CW / P25 / NXDN / DMR signal generator with internally adjustable power from 0 dBm to –120 dBm.
The S412E is Anritsu's second generation solution for installing and maintaining public safety systems. Built on Anritsu's ninth generation handheld platform, the S412E combines a high performance receiver / spectrum analyzer with the world's most advanced handheld vector network analyzer plus a CW / P25 / NXDN / DMR signal generator with internally adjustable power from 0 dBm to –120 dBm. The MT8212E and MT8213E Cell Master Base Station Analyzers are the smallest, lightest, and most economical solution for 2G/3G/4G, and WiMAX base station transmitter testing and ISDB-T and DVB-T/H digital broadcast field testing.
The MT8212E and MT8213E Cell Master Base Station Analyzers are the smallest, lightest, and most economical solution for 2G/3G/4G, and WiMAX base station transmitter testing and ISDB-T and DVB-T/H digital broadcast field testing. Anritsu’s handheld, battery-operated Broadband Site Master is the most accurate and convenient tool available for field installation, verification, troubleshooting and repair of microwave cables and communication systems. With calibrated vector error correction and a convenient user interface, difficult test specifications become easy to verify, quality is improved and maintenance expenses are reduced.
Anritsu’s handheld, battery-operated Broadband Site Master is the most accurate and convenient tool available for field installation, verification, troubleshooting and repair of microwave cables and communication systems. With calibrated vector error correction and a convenient user interface, difficult test specifications become easy to verify, quality is improved and maintenance expenses are reduced. The value choice for deploying, maintaining and troubleshooting wireless base stations. Compact and lightweight, it combines the functionality of built-in cable and antenna analyzer, spectrum analyzer, power meter, and GPS.
The value choice for deploying, maintaining and troubleshooting wireless base stations. Compact and lightweight, it combines the functionality of built-in cable and antenna analyzer, spectrum analyzer, power meter, and GPS. Anritsu introduces industry's most affordable, yet comprehensive solution, the MS2024B VNA Master (500 kHz to 4 GHz). It's a Vector Network Analyzer, it's a Power Meter and it's a Vector Voltmeter.
Anritsu introduces industry's most affordable, yet comprehensive solution, the MS2024B VNA Master (500 kHz to 4 GHz). It's a Vector Network Analyzer, it's a Power Meter and it's a Vector Voltmeter. Anritsu introduces broadband vector network analyzer with industry-best performance from 70 kHz to 110 GHz in single coax connection and up to 0.5 THz with millimeter waveguide extensions. ME7838A ushers in new era in broadband characterization of active and passive devices from DC to daylight.
Anritsu introduces broadband vector network analyzer with industry-best performance from 70 kHz to 110 GHz in single coax connection and up to 0.5 THz with millimeter waveguide extensions. ME7838A ushers in new era in broadband characterization of active and passive devices from DC to daylight. Anritsu Company introduces its first generation high performance PIM testing solution, the MW8208A, for the 850 MHz cellular frequency bands. Anritsu has developed the PIM Master to verify if receiver interference at a cell site is due to an intermodulation product of two or more transmit frequencies, also known as passive intermodulation (PIM).
Anritsu Company introduces its first generation high performance PIM testing solution, the MW8208A, for the 850 MHz cellular frequency bands. Anritsu has developed the PIM Master to verify if receiver interference at a cell site is due to an intermodulation product of two or more transmit frequencies, also known as passive intermodulation (PIM). Anritsu Company introduces its first generation high performance PIM testing solution, the MW8219A, for the 1900/2100 MHz PCS/AWS frequency bands. Anritsu has developed the PIM Master to verify if receiver interference at a cell site is due to an intermodulation product of two or more transmit frequencies, also known as passive intermodulation (PIM).
Anritsu Company introduces its first generation high performance PIM testing solution, the MW8219A, for the 1900/2100 MHz PCS/AWS frequency bands. Anritsu has developed the PIM Master to verify if receiver interference at a cell site is due to an intermodulation product of two or more transmit frequencies, also known as passive intermodulation (PIM). Anritsu Company introduces HSPA functionally for its MD8470A Signaling Tester that provides the MD8470A with best-in-class data rate analysis capability for HSPA applications. With the MX847010A-11 (HSDPA) and MX847010A-12 (HSUPA) options, the MD8470A is the only application test solution that can measure full HSPA data rates
Anritsu Company introduces HSPA functionally for its MD8470A Signaling Tester that provides the MD8470A with best-in-class data rate analysis capability for HSPA applications. With the MX847010A-11 (HSDPA) and MX847010A-12 (HSUPA) options, the MD8470A is the only application test solution that can measure full HSPA data rates Anritsu Company introduces the MA24106A, a highly accurate power sensor that measures True-RMS power, regardless of the input signal or its bandwidth, over 63 dB of dynamic range from 50 MHz to 6 GHz. Ideal for measuring average power of CW, multi-tone, and modulated RF waveforms, such as those used in 3G, 4G, and OFDM designs.
Anritsu Company introduces the MA24106A, a highly accurate power sensor that measures True-RMS power, regardless of the input signal or its bandwidth, over 63 dB of dynamic range from 50 MHz to 6 GHz. Ideal for measuring average power of CW, multi-tone, and modulated RF waveforms, such as those used in 3G, 4G, and OFDM designs. Anritsu Company introduces the MG37020A fast-switching microwave signal generator that utilizes an advanced VCO-based hardware architecture to achieve best-in-class frequency switching speed of 100 µsec per point.
Anritsu Company introduces the MG37020A fast-switching microwave signal generator that utilizes an advanced VCO-based hardware architecture to achieve best-in-class frequency switching speed of 100 µsec per point. Anritsu Company introduces test functions for W-CDMA mobile terminal UMTS bands XI (1.5 GHz) and III (1.8 GHz) for its ME7873F Performance Test System. With the expanded test capability, the ME7873F now offers mobile terminal carriers and manufacturers a comprehensive and simple test platform that supports all UMTS bands for testing the RF performance of user equipment.
Anritsu Company introduces test functions for W-CDMA mobile terminal UMTS bands XI (1.5 GHz) and III (1.8 GHz) for its ME7873F Performance Test System. With the expanded test capability, the ME7873F now offers mobile terminal carriers and manufacturers a comprehensive and simple test platform that supports all UMTS bands for testing the RF performance of user equipment. Anritsu Company introduces three software packages for its MS269xA Signal Analyzer Series. Taking full advantage of the MS269xA Series’ total level and modulation accuracy over the bandwidth from 50 Hz to 6 GHz, the MX269020A LTE Downlink Measurement Software, MX269021A LTE Uplink Measurement Software, and MX269908A LTE IQproducer™ help ensure compliance of LTE devices.
Anritsu Company introduces three software packages for its MS269xA Signal Analyzer Series. Taking full advantage of the MS269xA Series’ total level and modulation accuracy over the bandwidth from 50 Hz to 6 GHz, the MX269020A LTE Downlink Measurement Software, MX269021A LTE Uplink Measurement Software, and MX269908A LTE IQproducer™ help ensure compliance of LTE devices. Anritsu Company has enhanced its MS271xB family so that the economy microwave spectrum analyzers now provide specialized demodulation hardware and pre-written test routines for six popular wireless system configurations – Fixed and Mobile WiMAX, W-CDMA/HSDPA, cdmaOne, CDMA2000, EVDO, and GSM/GPRS/EDGE.
Anritsu Company has enhanced its MS271xB family so that the economy microwave spectrum analyzers now provide specialized demodulation hardware and pre-written test routines for six popular wireless system configurations – Fixed and Mobile WiMAX, W-CDMA/HSDPA, cdmaOne, CDMA2000, EVDO, and GSM/GPRS/EDGE. Anritsu Company introduces the MD8430A Signaling Tester, the industry’s first LTE base station simulator. Providing flexible and responsive support for the latest 3GPP LTE standard, the MD8430A is a highly accurate cost-effective solution for manufacturers of LTE chipsets and mobile devices to evaluate their products and improve time to market.
Anritsu Company introduces the MD8430A Signaling Tester, the industry’s first LTE base station simulator. Providing flexible and responsive support for the latest 3GPP LTE standard, the MD8430A is a highly accurate cost-effective solution for manufacturers of LTE chipsets and mobile devices to evaluate their products and improve time to market. Anritsu Company introduces the first test solutions that support next-generation PHS (XGP: eXtended Global Platform) to help ensure the successful rollout of XGP in the marketplace. Three software packages have been developed for use with Anritsu’s MS269xA Signal Analyzers and MG3700A Vector Signal Generator.
Anritsu Company introduces the first test solutions that support next-generation PHS (XGP: eXtended Global Platform) to help ensure the successful rollout of XGP in the marketplace. Three software packages have been developed for use with Anritsu’s MS269xA Signal Analyzers and MG3700A Vector Signal Generator. The Anritsu MS4640A Vector Network Analyzer offers a new level of performance for device modeling engineers struggling to accurately and reliably characterize their devices, for R&D engineers pushing the last fraction of a dB out of their state-of-the-art designs, and for the manufacturing engineer trying to maximize throughput without sacrificing accuracy.
The Anritsu MS4640A Vector Network Analyzer offers a new level of performance for device modeling engineers struggling to accurately and reliably characterize their devices, for R&D engineers pushing the last fraction of a dB out of their state-of-the-art designs, and for the manufacturing engineer trying to maximize throughput without sacrificing accuracy. Anritsu Introduces High Performance Handheld 2-Port Vector Network Analyzers. New VNA Master Models Have Frequency Coverage from 5 kHz to 20 GHz with 750 µsec/pt Measurement Speed To Ensure Accurate 2-Port Measurements.
Anritsu Introduces High Performance Handheld 2-Port Vector Network Analyzers. New VNA Master Models Have Frequency Coverage from 5 kHz to 20 GHz with 750 µsec/pt Measurement Speed To Ensure Accurate 2-Port Measurements. Highly Accurate Microwave USB Power Sensors with Range to 18 GHz Introduced by Anritsu Company. MA24108A / MA24118A Provide Accurate Power Measurements up to 18 GHz over 60 dB Dynamic Range and are Well Suited for Commercial and Aerospace / Defense Applications.
Highly Accurate Microwave USB Power Sensors with Range to 18 GHz Introduced by Anritsu Company. MA24108A / MA24118A Provide Accurate Power Measurements up to 18 GHz over 60 dB Dynamic Range and are Well Suited for Commercial and Aerospace / Defense Applications. Anritsu Co. introduces the MT8855A, an integrated test set capable of measuring the new generation of products using the Bluetooth Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP), headset profile and hands-free profile. Providing frequency coverage of 20 Hz to 20 kHz, the MT8855A offers lower cost-of-test and significantly reduced development time.
Anritsu Co. introduces the MT8855A, an integrated test set capable of measuring the new generation of products using the Bluetooth Advanced Audio Distribution Profile (A2DP), headset profile and hands-free profile. Providing frequency coverage of 20 Hz to 20 kHz, the MT8855A offers lower cost-of-test and significantly reduced development time. Anritsu Company, a global leader in LTE test solutions, introduces software packages for MG3700A and MS269xA Series Expand Anritsu LTE Test Offering; Anritsu Now Supports Both LTE Modes.
Anritsu Company, a global leader in LTE test solutions, introduces software packages for MG3700A and MS269xA Series Expand Anritsu LTE Test Offering; Anritsu Now Supports Both LTE Modes. Anritsu Company announces it has extended the low-end frequency of its MN469xB VectorStar 4-port test sets, making the instruments the first microwave multiport Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) solutions to measure down to 70 kHz. The MN469xB series now combines DC coverage and the wide dynamic range time domain capability of a VNA.
Anritsu Company announces it has extended the low-end frequency of its MN469xB VectorStar 4-port test sets, making the instruments the first microwave multiport Vector Network Analyzer (VNA) solutions to measure down to 70 kHz. The MN469xB series now combines DC coverage and the wide dynamic range time domain capability of a VNA. Cost-effective LTE fading simulator introduced by Anritsu Company. MF6900A is designed for use with MD8430A signaling tester and provides LTE terminal and chipset manufacturers with cost-efficient, accurate test solution.
Cost-effective LTE fading simulator introduced by Anritsu Company. MF6900A is designed for use with MD8430A signaling tester and provides LTE terminal and chipset manufacturers with cost-efficient, accurate test solution. P25 and NXDN measurement options for handheld spectrum analyzers introduced by Anritsu Company. Installers, maintainers, and certifiers of public safety and business communications systems have advanced test tool to ensure network operation.
P25 and NXDN measurement options for handheld spectrum analyzers introduced by Anritsu Company. Installers, maintainers, and certifiers of public safety and business communications systems have advanced test tool to ensure network operation. Anritsu Company introduces an on-screen coverage mapping option for its “E” Series Spectrum Master™, Site Master™ and Cell Master™ handheld analyzers. The option has been developed to help wireless service providers, public safety users, land mobile radio operators and government officials verify system coverage and perform spectrum clearing before installing new radio services.
Anritsu Company introduces an on-screen coverage mapping option for its “E” Series Spectrum Master™, Site Master™ and Cell Master™ handheld analyzers. The option has been developed to help wireless service providers, public safety users, land mobile radio operators and government officials verify system coverage and perform spectrum clearing before installing new radio services. Anritsu Company introduces the MS202xB/MS203xB VNA Master™ series, the highest-performing handheld RF vector network analyzers (VNAs) in the industry. With frequency coverage from 500 kHz to 4/6 GHz, and featuring multi-instrument functionality in a rugged, lightweight design that can withstand harsh environments.
Anritsu Company introduces the MS202xB/MS203xB VNA Master™ series, the highest-performing handheld RF vector network analyzers (VNAs) in the industry. With frequency coverage from 500 kHz to 4/6 GHz, and featuring multi-instrument functionality in a rugged, lightweight design that can withstand harsh environments. With companies looking for even greater efficiencies, the need to re-use not only hardware but software components is essential. Enormous investments in legacy systems cannot be disposed of so the ME7834 mobile device test platform provides the most flexible way to combine existing and new components.
With companies looking for even greater efficiencies, the need to re-use not only hardware but software components is essential. Enormous investments in legacy systems cannot be disposed of so the ME7834 mobile device test platform provides the most flexible way to combine existing and new components. Anritsu Company introduces a software option for its MD8480C W-CDMA/GSM Signaling Tester that enables testing for the latest W-CDMA/GSM devices supporting simultaneous 64QAM and MIMO. This release builds on existing W-CDMA/HSPA support in the MD8480C.
Anritsu Company introduces a software option for its MD8480C W-CDMA/GSM Signaling Tester that enables testing for the latest W-CDMA/GSM devices supporting simultaneous 64QAM and MIMO. This release builds on existing W-CDMA/HSPA support in the MD8480C. Anritsu will showcase test instruments for design, production, and installation/maintenance. On display will be the MG3690C series of broadband signal generators that covers audio, HF, VHF, UHF, RF and microwave frequencies from 0.1 Hz to 70 GHz in single coaxial output and up to 325 GHz or beyond, with external multipliers
Anritsu will showcase test instruments for design, production, and installation/maintenance. On display will be the MG3690C series of broadband signal generators that covers audio, HF, VHF, UHF, RF and microwave frequencies from 0.1 Hz to 70 GHz in single coaxial output and up to 325 GHz or beyond, with external multipliers Anritsu Company announces it has enhanced the LTE measurement capabilities in its MS272xC Spectrum Master™ and MT822xB BTS Master™ series of handheld analyzers. With the new analysis tools added to the existing measurement capabilities, field engineers and technicians have handheld instruments that can conduct nearly all the measurements necessary to successfully deploy, commission, and maintain LTE networks.
Anritsu Company announces it has enhanced the LTE measurement capabilities in its MS272xC Spectrum Master™ and MT822xB BTS Master™ series of handheld analyzers. With the new analysis tools added to the existing measurement capabilities, field engineers and technicians have handheld instruments that can conduct nearly all the measurements necessary to successfully deploy, commission, and maintain LTE networks. Anritsu Co. introduces software for its MS269xA and MS2830A series Signal Analyzers, as well as its MG3700A Vector Signal Generator to create single-instrument solutions that support the IEEE 802.11n/p/a/b/g/j wireless LAN (WLAN) standards.
Anritsu Co. introduces software for its MS269xA and MS2830A series Signal Analyzers, as well as its MG3700A Vector Signal Generator to create single-instrument solutions that support the IEEE 802.11n/p/a/b/g/j wireless LAN (WLAN) standards. Anritsu introduces PIM Master™ model for UMTS band VIII and LTE band 8 networks. The MW8209A brings inherent advantages of PIM Master, including distance-to-PIM technology, to E-GSM 900 MHz band.
Anritsu introduces PIM Master™ model for UMTS band VIII and LTE band 8 networks. The MW8209A brings inherent advantages of PIM Master, including distance-to-PIM technology, to E-GSM 900 MHz band. New-generation, eco-friendly signal analyzer supporting high-level measurement speeds and performance at low cost to help raise R&D efficiency and productivity.
New-generation, eco-friendly signal analyzer supporting high-level measurement speeds and performance at low cost to help raise R&D efficiency and productivity.