Cascade Microtech has developed WinCal 2006™ with new software tools to address the many testing challenges brought on by the increase in the volume of complex, high speed semiconductors that are designed for use in mobile communications products such as cell phones, PDAs and laptop computers. Compounding the multi-gigabit high speed requirement is the fact that lower operating voltage ICs are becoming increasingly susceptible to random bit errors forcing engineers to differential circuit designs to increase noise immunity. With this complexity comes an increased need to make accurate and repeatable multiport RF measurements on-wafer for design validation and to ensure they do not fail in production. Since the responsibility for testing often falls to the research and development team, many engineers must perform — for the first time — high frequency device characterization using a wafer probing station coupled with a multiport vector network analyzer (VNA).
Leveraging off of 20 years of on-wafer VNA calibration and measurement experience, WinCal 2006 software offers advanced tools that exceed the needs of today’s multiport VNA users. Multimedia tutorials, self-guided Wizards and pre-optimized quick set ups provide fast starts for both novices and experts. The highly interactive graphical user interface provides access and control to every element of the system — VNA, probes, calibration standards and all measurements. Fully automatic VNA calibrations using industry standard routines, or Cascade Microtech’s advanced, patented routines on par with the best NIST methods are provided at the click of a button. Enhanced reporting features allow operators to manipulate multiple sets of raw and calibrated data, standard measurements and VNA error correction terms, or transform them into H-, X-, Y- or differential S-parameters.
67 GHz Multiport On-wafer Measurement Challenges
The rise in the need for reliable differential millimeter-wave S-parameter measurements for circuit modeling gave advent to the multiport VNA. Today’s multiport VNA relies on four-port, single-ended S-parameters transformed mathematically to produce the needed differential S-parameters. This technique works well assuming the measurement ports are uncoupled error-corrected coaxial measurement ports. To produce the same single-mode coaxial TEM quality VNA measurement environment, metal-fingered multi-contact coplanar waveguide (CPW) probes have been replaced by Cascade Microtech’s patented thin film MIC tips, which reduces crosstalk from typically > 10 percent at 20 GHz for metal-finger probes to less than 1 percent at 67 GHz for thin film tips. Additionally, for the physically larger multiport calibration standards to maintain single-mode, uncoupled operation, it is necessary to use mode-suppressing elements on the substrate — developed and patent pending by Cascade Microtech — and prober auxiliary chucks proven to be mode-free beyond 110 GHz.
Calibration, Verification and Monitoring Are the Keys to Accurate Measurements
When performing on-wafer measurements above 50 GHz, there are many issues that can affect the accuracy and reliability of the data, including vector repeatability, probe contact planarity and contact cleanliness. At the heart of WinCal 2006 resides software tools designed to minimize and control all systematic errors and thus produce and maintain the environment for highest quality measurements yielding more accurate model extractions.
Under the System Qualification Tools, shown in Figure 1, operators now have access to tools that assure the mechanical integrity of all of the VNA test ports, cables and multi-contact RF probes testing each of these critical parameters. Probe contact planarity is critical to high frequency S-parameter measurements because the most frequent operational error prior to calibration is due to a lack of planarity. Ensuring contact cleanliness is important because contamination can and will accumulate with multiple device contacts during the measurement routine, which can cause intermittent test errors and inaccurate results.

Fig. 1 System qualification and reliability tools.
WinCal 2006 Repeatability Tools allow users to test the vector repeatability of all measurements necessary for calibration. At any time during calibration, a test can be performed to test the repeatability of all measurement ports, simultaneously, to ensure their stability, which is necessary for calibration. This test is done prior to calibration to ensure system integrity; the calibration will abort when repeatability is inadequate on any port.
Under the WinCal 2006 Calibration menu, users first define the number of VNA ports to calibrate, then select from a list of industry standard calibration methods such as SOLT, LRM or advanced algorithms such as SOLR or Cascade Microtech’s proprietary LRRM algorithm. In the case of the multiport VNA, WinCal 2006’s SOLT algorithm is optimized by the new reduced thru method allowing full correction from measurement of only four thrus instead of the previously required six. The reduced thru method minimizes the number of elements, definitions and moves, which speeds up the routine while reducing errors resulting from over-determination of standards. Once the calibration preferences are selected, WinCal 2006 will direct the probe station to move to the required standards, take raw S-parameter measurements, compute the VNA error terms and set the VNA corrections — all automatically. WinCal 2006 allows users to mark when structures have reached this limit, and retain the status of these bad structures. Once a structure is marked bad, the prober will never visit it again. WinCal 2006 will keep track of the good standards and the bad standards and manage the Impedance Standard Substrates (ISS) commonly used today (see Figure 2).

Fig. 2 Impedance standard substrate management tools for calibration.
WinCal 2006 Validation Tools, shown in Figure 3, allow the operator after calibration to check the corrected S-parameter of all the measurement ports against previously determined good measurements depending on their standard of choice. As with previous versions of WinCal, users can select from verification elements resident on Cascade Microtech’s Impedance Standard Substrates as the reference standard. However, with WinCal 2006, it is also possible for a user to compare current measurements to previously filed reference measurements, or better yet, can provide their own “golden device” as the reference standard for validation. This capability allows the utmost level of flexibility while maintaining the reliability and repeatability of high frequency S-parameter measurements.

Fig. 3 Port validation tools.
WinCal 2006 Monitoring Tools allow the user to measure the drift of any or all of the VNA ports simultaneously. User defined drift limits can be set for any or all S-parameters to monitor the stability of the VNA test system and assure the integrity of the resultant S-parameter measurements (see Figure 4). Any change to the VNA test system after calibration could cause the calibration to be invalid. With WinCal 2006’s monitoring tools, a user is notified in real-time when any port drifts past the defined drift limits.
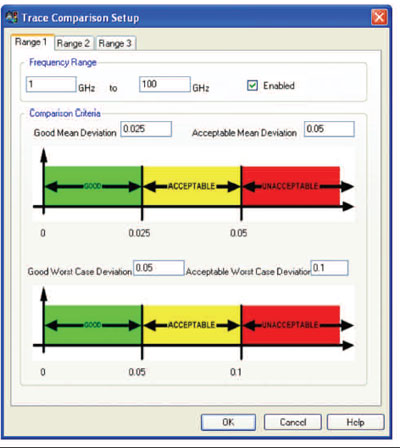
Fig. 4 User-defined drift limits for monitoring.
Conclusion
WinCal 2006 offers the most trustworthy and efficient vector network analyzer calibration available for metrology grade S-parameter measurement. Through on-line wizards and tutorials, it provides a fast start for new and experienced users. The enhanced validation capabilities as well as flexible reporting functions offer a higher level of confidence in RF measurements. WinCal 2006 was developed as the calibration platform for the future by allowing for customization and future functionality. Its ease-of-use will eliminate errors in the VNA calibration process in RF device characterization, and allow more users to make meaningful and valuable measurements.
Cascade Microtech Inc.,
Beaverton, OR
(503) 601-1000
www.cascademicrotech.com
