SUPPLIERS
So, who are the main global suppliers of RF BTB traditional coaxial connectors? Here is a short list of known suppliers:
- Amphenol RF
- HUBER+SUHNER AG
- Molex LLC
- Radiall S.A.
- Suzhou Recodeal Interconnection System Co., Ltd./ Suzhou Ruida Connection System Co., Ltd.
- TE Connectivity Ltd.
For traditional pogo pins, a truncated list of known suppliers is shown here:
- CFE Corporation Co., Ltd. (China)
- MILL-MAX Mfg. Corp. (U.S.)
- Shenzhen Rtench Technology Co., Ltd. (China)
- Suzhou Shengyifurui Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. (China)
- Yokowa Co., Ltd. (Japan)
We are unable to provide the supplier for the RF pogo pin solutions shown in Figures 6, 7 and 8.
RF BTB CONNECTORS - ALPHABET SOUP
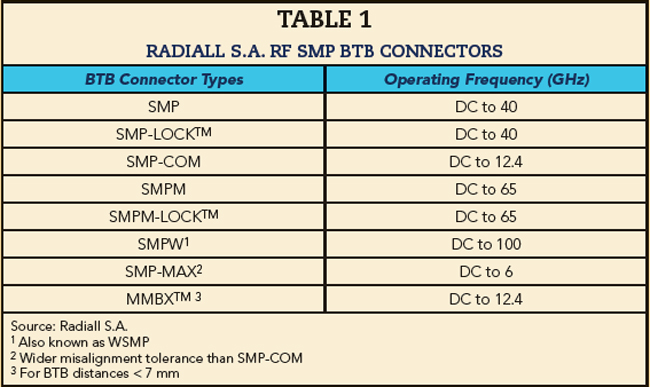
The designation of an RF SMP BTB connector is extremely broad as a family of products with numerous specific sub-types that are sometimes associated with the IP/design from a specific vendor. Size, cost, frequency of operation and misalignment tolerances typically dictate which type of RF SMP BTB connector solution is used within a radio system. Table 1 illustrates just a few of the many different types of RF SMP BTB connectors available from one major vendor.
Adding to the alphabet soup of the RF SMP BTB connector solutions are the CSMP variant that is usable up to 65 GHz, similar to the SMPM solution from Radiall, the ASMP variant that is usable up to 26.5 GHz, and the PSMP/P-SMP which operates up to 10 GHz and can handle 200 W of power.
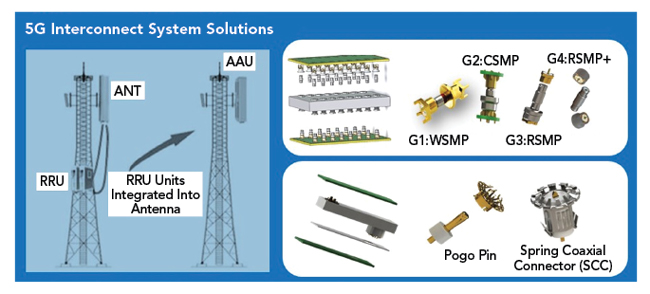
Figure 9 Suzhou Recodeal RF SMP BTB solutions for 5G (Source: Suzhou Recodeal Interconnection System Co., Ltd.).
The letter that is very interesting is “R.” The reachable SMP (RSMP) and RSMP+ variants have been developed by Suzhou Recodeal Interconnection System Co., Ltd. in China and awarded a patent and (to our knowledge) is only licensed to Changzhou Amphenol Fuyang Communication Equipment Co., Ltd. This deal excludes traditional European RF connector suppliers such as Rosenberger Hochfrequenztechnik GmbH & Co. KG, HUBER+SUHNER AG and Radiall S.A. (see Figures 9 through 11).
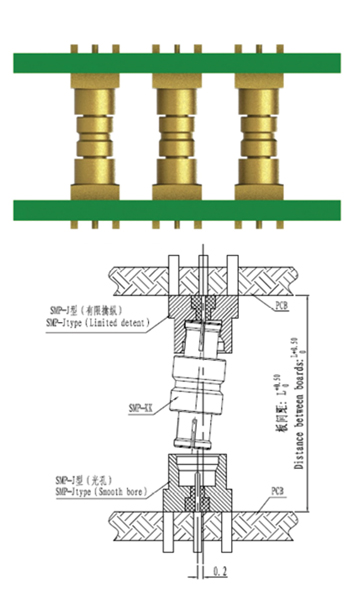
Figure 10 Suzhou Recodeal through hole RSMP RF BTB connector solution (Source: Suzhou Recodeal Interconnection System Co., Ltd.).

Figure 11 Amphenol SMT RSMP RF BTB Connector Solution (Source: Amphenol Fuyang).
MARKET OUTLOOK
While 5G deployments in the U.S. are expected to be mostly completed by the end of 2023 and continue to inch along in Europe, India has emerged as the next opportunity for 5G deployments. The first phase of the 5G networks for Bharti Airtel, Reliance Jio and Vodafone Idea will be supplied by RAN equipment vendors Ericsson, Nokia and Samsung Electronics as the Chinese OEMs, namely Huawei Technologies and ZTE, have been barred. While India, with its government and tech sector having high aspirations for a home-grown domestic Open RAN equipment ecosystem, has the potential vendors, their solutions remain unavailable until potentially the second phase of the 5G network deployments. The unique cost structure for RAN equipment in India will make it challenging for any Open RAN equipment vendor as well as RF connector and component suppliers to participate.
Regarding the 5G market in China, it has essentially been on hold for mMIMO antenna solutions since 2019 to 2020 when Huawei Technologies was put onto the Entity List by the U.S. Commerce Department’s Bureau of Industry and Security and banned from purchasing advanced U.S. semiconductor chips and access to U.S. developed/manufactured advanced semiconductor wafer fab equipment and foundry services. While Huawei had stockpiled a sizable amount of semiconductor application-specific ICs (ASICs) in anticipation of such action from the U.S., we believe that it has consumed the majority of these critical semiconductor chips over the past several years, biding time, perhaps until it can port its TSMC ASICs over to SMIC’s < 10 nm process nodes. We believe that such an event would trigger the ramp of 5G deployments again in China. Such a ramp would require 3 million+ 32 Tx and 64 Tx mMIMO radio antenna systems but with domestic Chinese/Taiwanese suppliers only and potentially with little to no BTB RF connector sockets available to non-Chinese/Taiwanese suppliers or at all if ZTE Corporation also converts to the use of RF pogo pin solutions.

.jpg?1679596290)