Splitting an RF input signal within a VCR or television was never much of a design challenge for manufacturers when the signal was analog. That changed dramatically, however, when CATV systems made the transition from analog to digital to provide addressability, video on demand, Internet access and other services. Today a broad array of performance specifications dictated by the Data Over Cable Service Interface Specification (DOCSIS) must be stringently met by all active devices in order to effectively transfer data via CATV. This challenge has been addressed with the CGA series of economical active three- and four-output active splitters that provide high linearity and isolation, and low power consumption.

The CGA family currently consists of the three-output CGA-0116 and the four-output CGA-0255 splitters. Both are fabricated with a silicon germanium heterojunction bipolar transistor (SiGe HBT) process that features 2 mm emitters. The patent-pending architecture of both devices centers on an emitter-follower input stage that provides high reverse isolation and common-emitter output stages that provide gain (typically 6 dB at 870 MHz). The gain is required to maintain the host product's signal-to-noise ratio, which would otherwise be degraded by the inherent loss of the splitter. The emitter resistor helps deliver stable gain performance over the operating temperature range of -40° to +85°C.
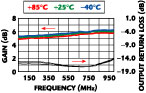
The CGA-0116 splitter is housed in a 16-pin TSSOP package and the CGA-0255 splitter is a 28-pin 5 mm x 5 mm QFN package. Both cover 50 to 900 MHz, have single-ended inputs and outputs, and operate from +5 VDC. They are internally matched to 75  , have a gain variation of ±0.5 dB, and isolation between ports is at least 42 dB in the CGA-0255 and at least 35 dB in the CGA-0116. A complete list of specifications is provided in Table 1 , and typical isolation and gain versus frequency for the CGA-0255 are shown in Figures 1 and 2 , respectively.
, have a gain variation of ±0.5 dB, and isolation between ports is at least 42 dB in the CGA-0255 and at least 35 dB in the CGA-0116. A complete list of specifications is provided in Table 1 , and typical isolation and gain versus frequency for the CGA-0255 are shown in Figures 1 and 2 , respectively.
The initial applications for the CGA series active splitters are set-top boxes. However, they are equally suited for cable modems, personal video recorders (PVR) and the home gateways that should begin to appear in quantity later this year. The four-output CGA-0255 was created in response to the emergence of set-top boxes with integrated PVRs that include two tuners (one for viewing and one for recording).
With either device, the 75  RF input enters the host product and is typically split off for DOCSIS data signals, broadcast video signals (both 256 QAM), digital only (usually for a PVR) and an "out-of-band" output that is fed straight through to an output on the host device that is generally used for a VCR or analog TV. A typical application is shown in Figure 3 .
RF input enters the host product and is typically split off for DOCSIS data signals, broadcast video signals (both 256 QAM), digital only (usually for a PVR) and an "out-of-band" output that is fed straight through to an output on the host device that is generally used for a VCR or analog TV. A typical application is shown in Figure 3 .
While Sirenza has extensive experience with GaAs HBT and silicon bipolar technologies as well as SiGe, the famously cost-sensitive characteristics of the consumer electronics market essentially dictated SiGe as the process of choice. SiGe devices are less expensive to produce than their GaAs counterparts, and offer the potential of achieving greater linearity, which is an essential characteristic in the multitone CATV signal environment.

The use of a single device rather than discrete components to split signals in CATV applications is a relatively new development. Manufacturers of set-top boxes have well-characterized low cost production capabilities optimized for assembly of various functions using discrete components. The splitter and required gain are commonly delivered with amplifier gain blocks or even discrete transistors and baluns.
The CGA series splitters offer significant advantages over the discrete approach, most notably a potential increase in yield, since all CGA series splitters are completely RF tested, effectively producing a "known good module" that is ensured of meeting the desired specifications. Using a single module also eliminates the potential for problems associated with the use of multiple components, including variances in their values and bad solder joints. In addition, the parts count is reduced, along with inspection and testing of multiple components. The design of new products can be simplified as well. High reliability is ensured since the devices are subjected to a complete battery of RF tests, including second- and third-order intercept point, return loss and isolation, as well as CATV-specific measurements such as composite second-order (CSO), composite triple beat (CTB) and cross modulation.
|
Table 1 | ||
|
|
CGA-0116 |
CGA-0255 |
|
Operating frequency (MHz) |
50 to 870 |
50 to 870 |
|
Maximum input power (dBm) |
15 |
15 |
|
Output power at 1 dB compression (at 500 MHz, dBμV) |
120 |
119 |
|
Small signal gain (870 MHz, dB) |
7.5 |
6.0* |
|
Input return loss (dB) |
9 |
14 |
|
Output return loss (dB) |
13 |
15 |
|
Third-order intercept point (500 MHz, dBμV) |
134 (output) |
129 (input)* |
|
Second-order intercept point (500 MHz, dBμV) |
155 (output) |
147 (input)* |
|
Noise figure (dB) |
7.5 |
6.5 |
|
Channel-to-channel isolation (dB) |
35 |
42 |
|
Gain response (dB) |
±0.5 |
±0.5 |
|
Impedance (W) |
75 |
75 |
|
Power supply (mA at 5 VDC) |
200 |
275 |
|
Package |
TSSOP-16 |
QFN |
|
*Channels 1 to 4. | ||
The small size of the CGA series also reduces the required circuit board "real estate" required to implement the splitting function. This should be most appealing in new set-top box designs incorporating PVRs, as well as entirely new product types such as home gateways that allow distribution within the home of high speed Internet access, voice over IP telephony, video on demand and other services.
While the CGA-0116 and CGA-0255 splitters have single-ended inputs and outputs, future models in the series will have single-ended or differential inputs and differential outputs with gain control. These developments are a direct response to the coming change in television tuner design. While tuners have evolved over the years from massive mechanical contrivances to synthesized solid-state types that are a fraction of the size and weight, the typical television tuner today remains an electromechanical device that uses many discrete, hand-assembled components, and is inexpensive to produce only because of its place of construction, typically Eastern Europe or Asia.
The coming generation of solid-state tuners will dramatically reduce tuner complexity to a single ASIC module along with a few peripheral components that together are orders of magnitude smaller than current solutions. These small, low cost, power-efficient splitters are ideally suited for the wide array of consumer devices that will soon use these tuners. Ultimately, the major components of a set-top box/PVR might only include a splitter, single-chip tuner(s), power supply and hard drive, along with a few other inexpensive devices.
The CGA family is part of a growing family of devices designed for CATV applications. In addition to the splitters, the family currently includes the CGA-3318 SiGe HBT and CGA-6618 InGaP broadband amplifiers in SOIC-8 packages for head-end driver and predriver applications. Both devices are push-pull configurations for excellent second-order intercept performance, operate from a single 5 VDC supply, and have dropping resistors for temperature compensation.
The CGA-0116 three-output active splitter is in production and available for immediate delivery. The CGA-0255 is currently available in sample quantities. Evaluation boards with F connectors for RF and pins connections for bias are available for both products.
Sirenza Microdevices , Broomfield, CO (800) 764-6642, e-mail: info@sirenza.com, Web site: www.sirenza.com.
Circle No. 301
