Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) has the potential to power a range of new applications collecting and sharing personal fitness and health management data, but delays in product deliveries to markets over the past 12 months have some application developers looking to rival technologies and protocols. The Bluetooth SIG did not formally adopt the Bluetooth Core Specification Version 4.0 which encompasses Bluetooth Low Energy technology until July 2010 – more than six months later than many in the industry had expected.
With the huge potential of the Bluetooth Low Energy technology, the wait for adoption by the Bluetooth SIG has put a brake on many wireless health and sports devices’ market launches. Where it has not halted product development it has fostered adoption of rival traditional Bluetooth and proprietary offerings in the market. In addition, application developers have looked to build offerings around smartphone handsets’ current sensor and data collection capabilities. However, ABI Research believes that Bluetooth Low Energy remains of key importance to the proliferation and adoption of wearable wireless-enabled sports and health sensors.
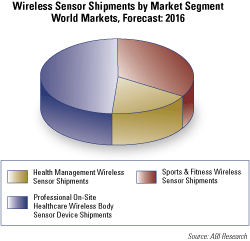
ABI Research’s “Wireless Healthcare and Fitness Market Data” provides forecast data for a number of significant types of wireless equipment in a healthcare environment including Wi-Fi access points and Wi-Fi RTLS appliances. It includes examination of remote patient monitoring, telehealth and telepresence, and contains data about “body area networks.”
This product is included in the firm’s Wireless Healthcare Research Service, which also includes Research Reports, a home security Survey, ABI Insights, and analyst inquiry support.
