Texas Instruments (TI) worked with NASA and other industry experts to lead the development of Qualified Manufacturers List (QML) Class P, a new plastic packaging standard for space electronics. Electronics in space must meet government standards set forth in the QML, ranging from radiation-tolerant or radiation-hardened devices in either ceramic or plastic packaging. The QML assures that parts will operate as intended in harsh space environments.
TI’S SPACE PORTFOLIO
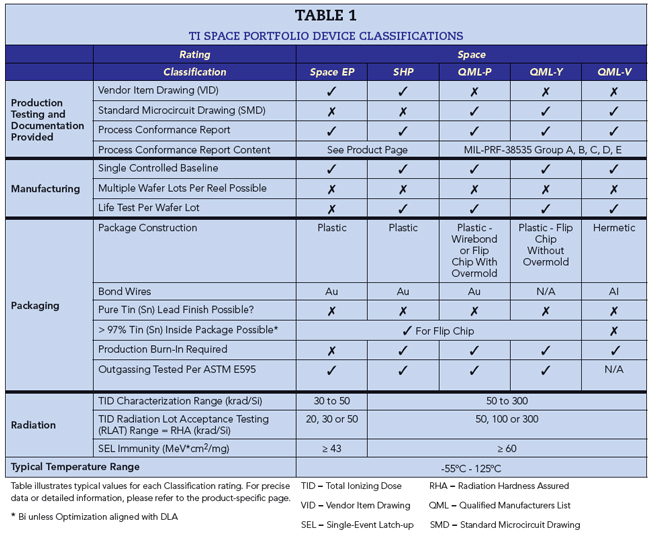
QML Class P is a packaging standard that TI recently added to its portfolio of space products. It defines the qualification flow used for radiation-hardened semiconductors in plastic packages. TI spearheaded the initiative, along with NASA and other industry experts, to create the QML Class P standard. Table 1 shows the different ratings TI offers for mission quality requirements, ranging from new space to deep space, in low Earth orbit, medium Earth orbit and geostationary orbit applications.
THE NEED FOR QML CLASS P
The use of plastic packages is not new in space applications. However, the lack of a QML standard in the industry meant that there was no standard assurance that radiation-hardened products in plastic packages would operate as intended in the harsh environments of space. That situation has changed with the development of the QML Class P standard and products.
Table 1 illustrates how QML Class P products follow a similar qualification flow to QML Class V products. The 100 percent production burn-in and the standard microcircuit drawing make QML Class P products almost compatible with QML Class V products, with the added benefits that plastic packages offer. The usage of gold bond wires and outgassing tests, according to the American Standard of Testing and Materials E595, address concerns specifically related to plastic packages.
BENEFITS OF QML CLASS P
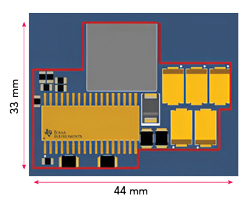
Figure 1 Board layout using the TPS7H4001-SP buck converter in the QML Class V package.
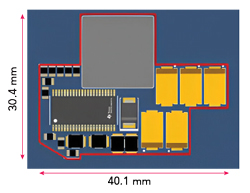
Figure 2 Board layout using the TPS7H4001-SP buck converter in the QML Class P package.
QML Class P offers multiple benefits to engineers working on space applications. The most obvious benefit is the reduction in package size. Plastic packages for QML Class P products are as much as 50 percent smaller while still having increased power density, translating to an area reduction at the power converter level.
For example, TI’s TPS7H4001-SP is an 18 A buck converter offered in both QML Class V and QML Class P packages. One of this buck converter’s functions is to power up high performance field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs) in space applications. For both the QML Class V and QML Class P packages shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2, respectively, the design of the board using the TPS7H4001-SP has an input voltage of 5 V and an output voltage of 1 V with 18 A of current, at a switching frequency of 500 kHz. The actual converter area, shown inside the red lines of Figure 1 and Figure 2 for the QML Class V version, is 11 cm2, while the converter area for the QML Class P version is 8.7 cm2. Using QML Class P enables tighter placement of the passive components around the package. QML Class P also offers pin-to-pin compatibility between radiation-tolerant and radiation-hardened products, removing the need for hardware changes when moving from one type of application to another.
Finally, because of the plastic materials and construction, QML Class P packages offer lower parasitic resistance, inductance and capacitance. The performance in these areas translates to improved electrical performance compared to ceramic QML Class V packages. The bond wires in plastic packages are smaller and shorter, resulting in lower resistance and inductance.
QML CLASS P PORTFOLIO
QML Class P expands TI’s current portfolio of radiation-tolerant and radiation-hardened products in plastic and ceramic packages. TI has released these QML Class P products for use across spacecraft electrical power systems:
- TPS7H5001-SP is a pulse width modulator controller supporting advanced power topologies using silicon and GaN field-effect transistors
- TPS7H4001-SP is a 7 V, 18 A buck converter used to power up high performance FPGAs
- TPS7H1111-SP is a low dropout (LDO) linear regulator with low output noise and a high power supply rejection ratio
- TPS7H3302-SP is a 3 A sink-and-source double data rate termination LDO regulator
- TPS7H2201-SP is a 7 V, 6 A eFuse
- TPS7H2211-SP is a 14 V, 3.5 A eFuse.
Use cases range from high voltage applications in spacecraft solar panels to point-of-load payload applications.
CONCLUSION
The realization of the QML Class P plastic packaging standard is a step forward in solving some of the challenges engineers face in space applications. Leveraging the significant advances in semiconductor technology and applying them to space applications enables faster development to accelerate space exploration.
For more information, see ti.com/space.
Texas Instruments
Dallas, Texas
www.ti.com
